Jupiter‘s Nice Purple Spot (GRS) is without doubt one of the Photo voltaic System’s defining options. It is a huge storm that astronomers have noticed because the 1600s.
Nonetheless, its date of formation and longevity are up for debate. Have we been seeing the identical phenomenon all this time?
The GRS is a big anti-cyclonic (rotating counter-clockwise) storm that is bigger than Earth. Its wind speeds exceed 400 km/h (250 mp/h). It is an icon that people have been observing since a minimum of the 1800s, probably earlier. Its historical past, together with the way it fashioned, is a thriller.
Its earliest observations could have been in 1632 when a German Abbott used his telescope to take a look at Jupiter. 32 years later, one other observer reported seeing the GRS shifting from east to west. Then, in 1665, Giovanni Cassini examined Jupiter with a telescope and famous the presence of a storm on the similar latitude because the GRS. Cassini and different astronomers noticed it repeatedly till 1713 and he named it the Everlasting Spot.
Sadly, astronomers misplaced observe of the spot. No one noticed the GRS for 118 years till astronomer S. Schwabe noticed a transparent construction, roughly oval and on the similar latitude because the GRS.
Some consider that statement as the primary statement of the present GRS and that the storm fashioned once more on the similar latitude. However the particulars fade the additional again in time we glance. There are additionally questions concerning the earlier storm and its relation to the present GRS.
New analysis in Geophysical Analysis Letters mixed historic information with pc simulations of the GRS to attempt to perceive this chimerical meteorological phenomenon. Its title is “The Origin of Jupiter’s Nice Purple Spot,” and the lead writer is Agustín Sánchez-Lavega. Sánchez-Lavega is a Professor of Physics on the College of the Basque Nation in Bilbao, Spain. He is additionally head of the Planetary Sciences Group and the Division of Utilized Physics on the College.
“Jupiter’s Great Red Spot (GRS) is the largest and longest-lived known vortex of all solar system planets, but its lifetime is debated, and its formation mechanism remains hidden,” the authors write of their paper.
“From the measurements of sizes and movements we deduced that it is highly unlikely that the current GRS was the PS observed by G. D. Cassini. The PS probably disappeared sometime between the mid-18th and 19th centuries, in which case we can say that the longevity of the Red Spot now exceeds 190 years at least,” stated lead writer Sánchez-Lavega.
The GRS was 39,000 km lengthy in 1879 and has shrunk to 14,000 km since then. It is also turn out to be extra rounded.
The historic file is effective, however we now have totally different instruments at our disposal now. Area telescopes and spacecraft have studied the GRS in ways in which would’ve been unimaginable to Cassini and others. NASA’s Voyager 1 captured our first detailed picture of the GRS in 1979, when it was simply over 9,000,000 km from Jupiter.
Since Voyager’s picture, the Galileo and Juno spacecraft have each imaged the GRS. Juno, specifically, has given us extra detailed photos and information on Jupiter and the GRS. It captured photos of the planet from solely 8,000 km above the floor. Juno takes uncooked photos of the planet with its Junocam, and NASA invitations anybody to course of the photographs, resulting in clever photos of the GRS just like the one under.
Juno additionally measured the depth of the GRS, one thing earlier efforts could not obtain.
Just lately, “various instruments on board the Juno mission in orbit around Jupiter have shown that the GRS is shallow and thin when compared to its horizontal dimension, as vertically it is about 500 km long,” defined Sánchez-Lavega.
Jupiter’s environment accommodates winds working in reverse instructions at totally different latitudes. North of the GRS, winds blow in a westerly route and attain speeds of 180 km/h. South of the GRS, the winds move in the other way at speeds of 150 km/h. These winds generate a strong wind shear that fosters the vortex.
Of their supercomputer simulations, the researchers examined totally different forces that would produce the GRS in these circumstances. They thought of the eruption of a big superstorm like the sort that occurs, although hardly ever, on Saturn.
Additionally they examined the phenomenon of smaller vortices created by the wind shear that merged collectively to type the GRS. Each of these produced anti-cyclonic storms, however their shapes and different properties did not match the present GRS.
“From these simulations, we conclude that the super-storm and the mergers mechanisms, although they generate a single anticyclone, are unlikely to have formed the GRS,” the researchers write of their paper.
The authors additionally level out that if both of those had occurred, we must always’ve seen them.
“We also think that if one of these unusual phenomena had occurred, it or its consequences in the atmosphere must have been observed and reported by the astronomers at the time,” stated Sánchez-Lavega.
Nonetheless, different simulations proved extra correct in reproducing the GRS. Jupiter’s winds are recognized to have instabilities known as the South Tropical Disturbance (STrD). When the researchers carried out supercomputer simulations of the STrD, they created an anti-cyclonic storm similar to the GRS. The STrD captured the totally different winds within the area and trapped them in an elongated shell just like the GRS.
“We therefore propose that the GRS generated from a long cell resulting from the STrD, that acquired coherence and compactness as it shrank,” the authors write.
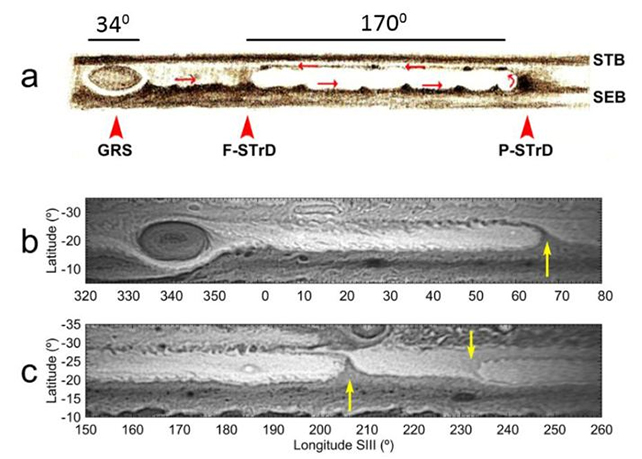
The simulations present that over time, the GRS would rotate extra quickly because it shrank and have become extra coherent and compact till the elongated cell extra carefully resembled the present GRS. Since that is what the GRS seems like now, the researchers settled on this rationalization.
That course of doubtless started within the mid-1800s when the GRS was a lot bigger than it’s now. That results in the conclusion that the GRS is just about 150 years previous.
This text was initially revealed by Universe Right now. Learn the unique article.

