Researchers will not want to decide on between learning a single human mind as a patchwork of fragmented pictures or a distant, pixelated view of huge constructions.
A brand new imaging platform developed by a US staff as an alternative seamlessly combines the finer particulars of mind cells, their connections and contents, with brain-wide maps of entire networks of neurons holding up the mind’s general structure.
These parts of mind biology exist on wildly completely different scales, from the nanometer-sized gaps of synapses to centimeter-long mind areas, which have till now required a number of samples from a number of brains to research utilizing varied applied sciences on completely different platforms.
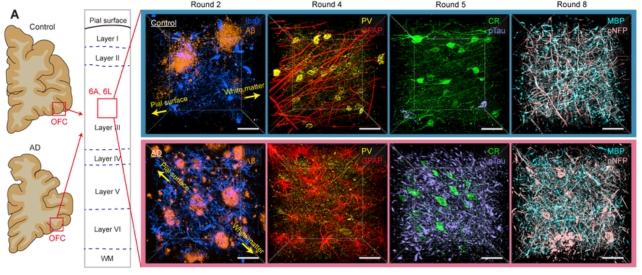
In its first demonstrated use on human tissue, imaging two entire brains, the platform has revealed distinct adjustments within the mind of 1 individual with Alzheimer’s illness.
The brand new platform contains three core parts to slice, course of, after which picture mind tissues with “unprecedented resolution and speed”, in accordance with the analysis staff that developed it, led by Kwanghun Chung, a chemical engineer at Massachusetts Institute of Know-how (MIT).
First, an modern system slices mind tissue into sections. It makes use of fastidiously tuned vibrations to keep away from abrasion, separating cells cleanly as extremely skinny slices with out dislocating their connections.
Then a chemical method reversibly transforms these tissue sections right into a stretchy, expandable tissue-hydrogel ripe for antibody tagging and high-resolution imaging of proteins and different inner issues.
Lastly, a computational instrument ‘stitches’ the sliced tissues again collectively and maps the connections between particular person cells. These ‘projectomes’ of single mind cells can then be built-in with profiles capturing the molecules expressed in every cell.
“We need to be able to see all these different functional components – cells, their morphology and their connectivity, subcellular architectures, and their individual synaptic connections – ideally within the same brain” to have the ability to evaluate entire brains and discover particular person variations, says Chung.
“This technology pipeline really enables us to extract all these important features from the same brain in a fully integrated manner.”
The tissue-turned-hydrogel gently inflates tissue sections to allow them to be imaged clearly; and a pump steadily infuses the tissues with fluorescent dyes to provide constant staining throughout entire organs.
In a dizzying show of the platform’s imaging capabilities, the researchers present examples the place they labeled one entire mind hemisphere, then zoomed in to take a snapshot of cell circuits, adopted by single cells and their connections throughout junctions referred to as synapses.
frameborder=”0″ allow=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share” referrerpolicy=”strict-origin-when-cross-origin” allowfullscreen>
As for how the platform reconstructs those connections across multiple tissue sections, the computer tool has an algorithm that matches blood vessels exiting one layer and entering the adjacent one, and traces the extensions of neighboring neurons, called axons.
Placing all of it collectively, the researchers imaged the entire brains of two beneficiant donors, one with Alzheimer’s illness and one with out.
They uncovered the same old pathological options of Alzheimer’s, together with the buildup of amyloid plaques and tau tangles, and shriveling mind cells, however their imaging additionally captured some finer variations.
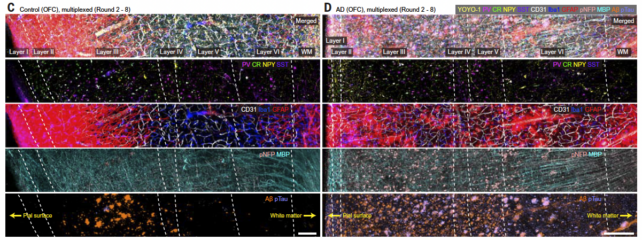
The axons of mind cells within the Alzheimer’s affected person have been swollen. Mind cells in areas laden with tau and amyloid proteins had additionally misplaced their protecting myelin protecting and withdrawn from their neighbors.
This “supports neuroimaging studies that suggest severe damage to the connectivity of the orbitofrontal cortex in the late stages of Alzheimer’s disease,” the staff writes of their paper.
Nevertheless, this gallery represents just one snapshot in time of simply two brains.
frameborder=”0″ allow=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share” referrerpolicy=”strict-origin-when-cross-origin” allowfullscreen>
Scientists have produced some remarkably detailed pictures of the human mind recently, zooming in on a single cubic millimeter of mind tissue – a decade-long effort that finally produced 1.4 petabytes of information.
Imaging how the mind adjustments because it slowly degenerates in illnesses like Alzheimer’s is a considerably more durable process as a result of researchers are sometimes working with autopsy mind tissues donated on the finish of somebody’s life, or counting on conventional whole-brain scans equivalent to MRI, hoping to detect adjustments earlier than the illness units in.
It is also not clear but how the platform may adapt to advances in mind imaging which might be quickly unfolding, however the staff is optimistic that their system will assist spur the event of latest therapies and maximize the quantity of data extracted from useful donor tissues.
“This pipeline allows us to have almost unlimited access to the tissue,” Chung says. “We can always go back and look at something new.”
The examine has been printed in Science.

