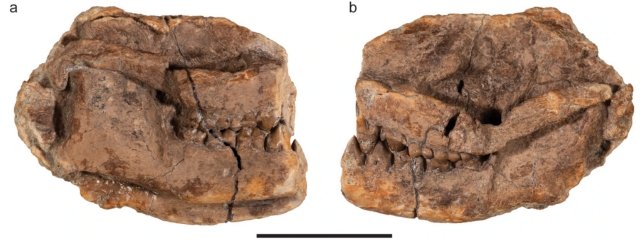
Meet the newly found species Militocodon lydae: Regarded as concerning the dimension of a rat and weighing as much as 455 grams or 16 ounces, this small mammal is the probably ancestor of all fashionable hoofed animals, known as ungulates.
The animal would have lived round 65 million years in the past, showing simply after the extinction of the dinosaurs, and was recognized from a part of a cranium and jawbone recovered from the Corral Bluffs, a fossil web site in Colorado.
In keeping with the researchers behind the invention, the creature fills some vital gaps in our information of the Periptychidae household of early mammals, which ascended after the dinosaurs‘ departure.
“The discovery and thorough descriptions and comparisons of the partial M. lydae skull represent an important step toward unraveling the complex evolutionary history of periptychid mammals,” paleontologist Lucas Weaver of Kent State College in Ohio and colleagues write of their revealed paper.
After unearthing the specimen and cleansing it up, the staff used subtle scanning methods, 3D reconstructions, and enamel comparisons – measuring them in opposition to enamel from different fossils and modern-day animals – to place M. lydae in the suitable place on the evolutionary tree.
Key to the analysis was proof that the animal’s enamel had been used to shear and crush somewhat than grind. That implies the small creature would finally result in the cows, pigs, and deer we now have at this time.
The researchers have solely discovered a handful of M. lydae fossils throughout the final eight years, so additional discoveries and research are nonetheless wanted to substantiate that this small and somewhat cute-looking animal is certainly what we predict it’s.
“The continued discovery and study of early Paleocene archaic ungulates will almost certainly reveal more specimens that do not fit neatly into existing taxonomic bins, forcing us to contend with an evolutionary history tangled by evolutionary grades and transitional forms,” the researchers write.
Every new fossil discovery provides researchers an opportunity to refine and rethink the sample of evolution on Earth – nearly like the larger image comes into sharper focus each time a brand new discover is analyzed.
Tracing the evolution of animals straight after the demise of the dinosaurs has been difficult for consultants due to a paucity of fossils from this time. The Corral Bluffs web site, which paleontologists have been excavating for many years, is proving more and more useful in serving to to deal with that downside.
It could have been a time of speedy and widespread diversification within the animal kingdom, however notably for mammals. After the mud settled from the asteroid impression, and with the dinosaurs out of the best way, mammals like M. lydae took the chance to thrive.
“Rocks from this interval of time have a notoriously poor fossil record,” explains Denver Museum of Nature & Science paleontologist Tyler Lyson, who led the analysis staff.
“The discovery and description of a fossil mammal skull is an important step forward in documenting the earliest diversification of mammals after Earth’s last mass extinction.”
The analysis has been revealed within the Journal of Mammalian Evolution.

