Hurricane Milton went from barely hurricane power to a harmful Class 5 storm in lower than 24 hours because it headed throughout the Gulf of Mexico towards Florida.
As its wind pace elevated, Milton turned one of the crucial quickly intensifying storms on file. And with 180 mph sustained winds on Oct. 7, 2024, and really low strain, it additionally turned one of many strongest storms of the 12 months.
Lower than two weeks after Hurricane Helene’s devastating influence, this type of storm was the very last thing Florida wished to see. Hurricane Milton was anticipated to make landfall as a serious hurricane late on Oct. 9 or early Oct. 10 and had already prompted widespread evacuations.
So, what precisely is speedy intensification, and what does international local weather change must do with it? We analysis hurricane conduct and educate meteorology. This is what you should know.
What’s speedy intensification?
Fast intensification is outlined by the Nationwide Climate Service as a rise in a tropical cyclone’s most sustained wind pace of at the very least 30 knots – about 35 mph inside a 24-hour interval. That enhance will be sufficient to escalate a storm from Class 1 to Class 3 on the Saffir-Simpson scale.
Milton’s wind pace went from 80 mph to 175 mph from 1 pm Sunday to 1 pm Monday, and its strain dropped from 988 millibars to 911.
The Nationwide Hurricane Heart had been warning that Milton was more likely to change into a serious hurricane, however this type of speedy intensification can catch folks off guard, particularly when it happens near landfall.
Hurricane Michael did billions of {dollars} in injury in 2018 when it quickly intensified right into a Class 5 storm simply earlier than hitting close to Tyndall Air Drive Base within the Florida Panhandle. In 2023, Hurricane Otis’ most wind pace elevated by 100 mph in lower than 24 hours earlier than it hit Acapulco, Mexico. Hurricane Ian additionally quickly intensified in 2022 earlier than hitting simply south of the place Milton is projected to cross Florida.
What causes hurricanes to quickly intensify?
Fast intensification is troublesome to forecast, however there are a couple of driving forces.
- Ocean warmth: Heat sea floor temperatures, notably after they prolong into deeper layers of heat water, present the power crucial for hurricanes to accentuate. The deeper the nice and cozy water, the extra power a storm can draw upon, enhancing its power.
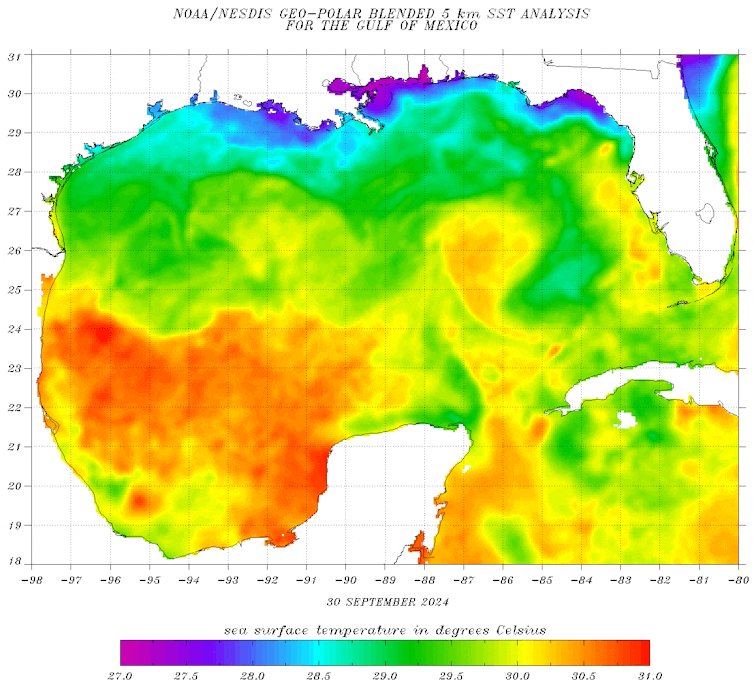
- Low wind shear: Robust vertical wind shear – a speedy change in wind pace or path with top – can disrupt a storm’s group, whereas low wind shear permits hurricanes to develop extra quickly. In Milton’s case, the atmospheric circumstances have been notably conducive to speedy intensification.
- Moisture: Larger sea floor temperatures and decrease salinity enhance the quantity of moisture out there to storms, fueling speedy intensification. Hotter waters present the warmth wanted for moisture to evaporate, whereas decrease salinity helps entice that warmth close to the floor. This permits extra sustained warmth and moisture to switch to the storm, driving sooner and stronger intensification.
- Thunderstorm exercise: Inside dynamics, akin to bursts of intense thunderstorms inside a cyclone’s rotation, can reorganize a cyclone’s circulation and result in speedy will increase in power, even when the opposite circumstances aren’t supreme.
Analysis has discovered that globally, a majority of hurricanes Class 3 and above are inclined to endure speedy intensification inside their lifetimes.
How does international warming affect hurricane power?
If it appears as if you’ve got been listening to about speedy intensification much more lately, that is partly as a result of it is taking place extra typically.
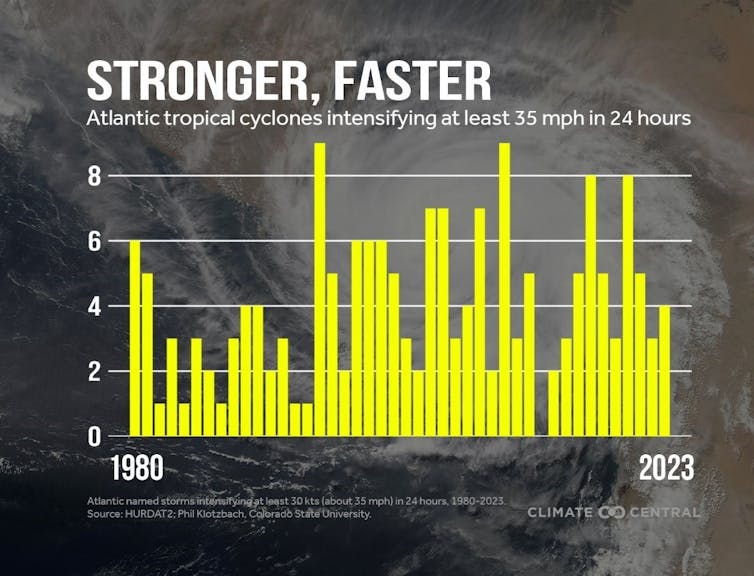
A 2023 research investigating connections between speedy intensification and local weather change discovered a rise within the variety of tropical cyclones experiencing speedy intensification over the previous 4 many years. That features a important rise within the variety of hurricanes that quickly intensify a number of instances throughout their growth.
One other evaluation evaluating tendencies from 1982 to 2017 with local weather mannequin simulations discovered that pure variability alone couldn’t clarify these will increase in quickly intensifying storms, indicating a possible function of human-induced local weather change.
How future local weather change will have an effect on hurricanes is an energetic space of analysis. As international temperatures and oceans proceed to heat, nevertheless, the frequency of main hurricanes is projected to extend. The acute hurricanes of current years, together with Beryl in June 2024 and Helene, are already elevating alarms concerning the intensifying influence of warming on tropical cyclone conduct.![]()
Zachary Handlos, Atmospheric Science Educator, Georgia Institute of Know-how and Ali Sarhadi, Assistant Professor of Atmospheric Science, Georgia Institute of Know-how
This text is republished from The Dialog below a Artistic Commons license. Learn the unique article.

