First Picket Satellite tv for pc Will Check ‘Green’ House Exploration
Japan’s LignoSat will check wooden’s resilience in area and will result in a brand new period of extra sustainable, much less polluting satellites
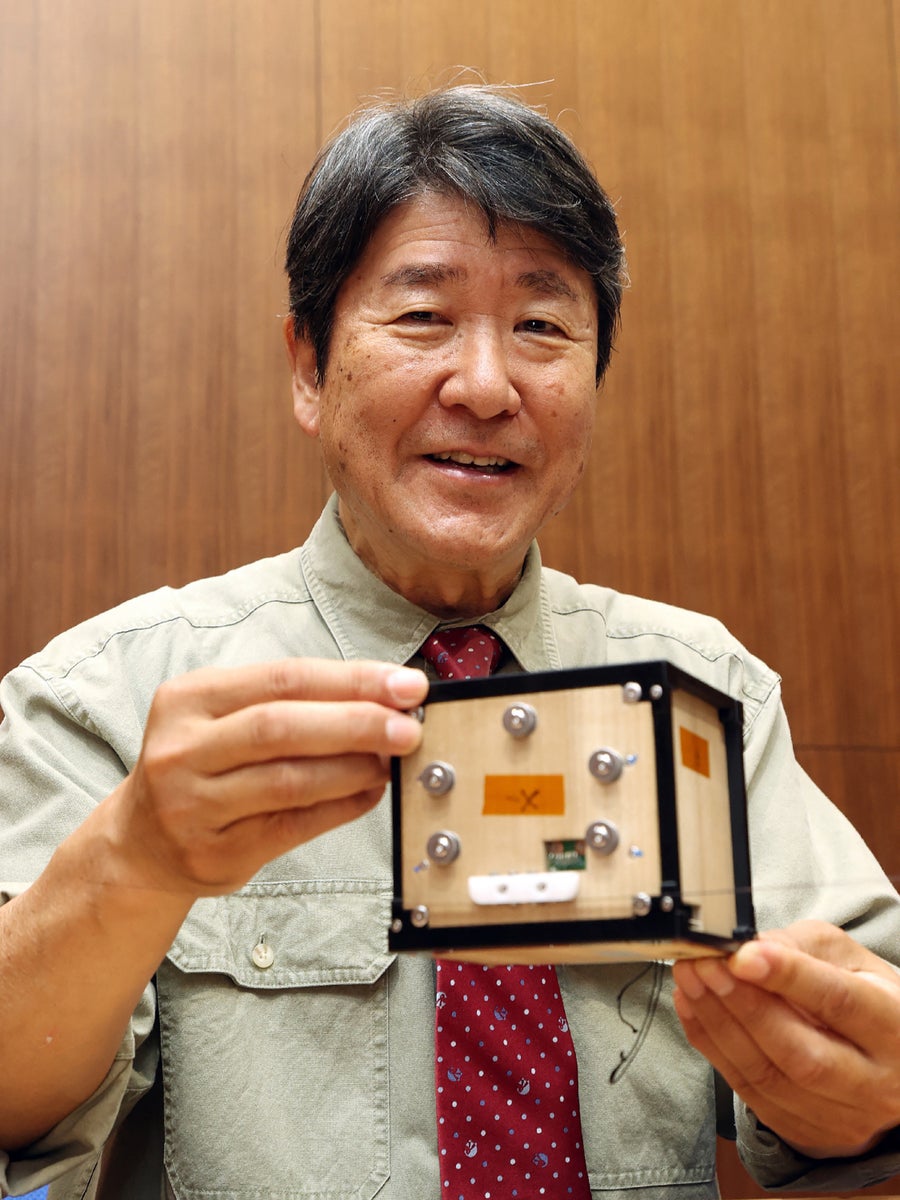
The world’s first satellite tv for pc produced from wooden and named LignoSat, developed by scientists at Kyoto College and logging firm Sumitomo Forestry, is proven throughout a press convention at Kyoto College in Kyoto on Could 28, 2024.
JiJi Press/AFP by way of Getty Photos
Researchers unveiled the world’s first picket satellite tv for pc final month, billing it as clearing a path for extra makes use of of wooden in outer area. The fabric will probably be extra sustainable and fewer polluting than the metals utilized in typical satellites, they are saying.
Researchers at Kyoto College in Japan and the Tokyo-based logging firm Sumitomo Forestry confirmed off the satellite tv for pc, known as LignoSat, in late Could. The roughly 10-centimetre-long dice is fabricated from magnolia-wood panels and has an aluminium body, photo voltaic panels, circuit boards and sensors. The panels incorporate Japanese wood-joinery strategies that don’t depend on glue or metallic fittings.
Wooden might sound counterintuitive to be used in area as a result of it’s flamable — however that characteristic could be fascinating. To curb the rising downside of area junk threatening spacecraft and area stations, rocket phases and satellites are intentionally plunged into the Earth’s environment to dissipate. However throughout combustion, they launch particles of aluminium and different metals. Many extra spacecraft launches are deliberate, and scientists have warned that the environmental results of this air pollution are unknown.
On supporting science journalism
In case you’re having fun with this text, think about supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By buying a subscription you might be serving to to make sure the way forward for impactful tales in regards to the discoveries and concepts shaping our world right this moment.
When LignoSat plunges again to Earth, after six months to a 12 months of service, the magnolia will incinerate utterly and launch solely water vapour and carbon dioxide, says Takao Doi, an astronaut and engineer at Kyoto College, who’s a part of the analysis staff. He factors to different advantages of wooden: it’s resilient within the harsh atmosphere of area and doesn’t block radio waves, making it appropriate for enclosing an antenna.
And there’s a precedent for spacecraft with picket components. Launched in 1962, NASA’s Ranger 3 lunar probe had a balsa-wood casing meant to guard its capsule because it landed on the lunar floor (the probe malfunctioned, missed the Moon and commenced orbiting the Solar).
Timber pioneers
LignoSat will price about US$191,000 to design, manufacture, launch and function. Sensors onboard will consider pressure on the wooden, temperature, geomagnetic forces and cosmic radiation, in addition to obtain and transmit radio indicators. The satellite tv for pc has been handed over to the Japan Aerospace Exploration Company (JAXA) and will probably be transferred to the Worldwide House Station in September, earlier than being launched into orbit in November.
Takao Doi, an astronaut and particular professor at Kyoto College, holds the world’s first satellite tv for pc produced from wooden and named LignoSat.
JiJi Press/AFP by way of Getty Photos
Development has been sluggish for the mission, which started in 2020 with hypothesis in regards to the wider potential for wooden in area for higher sustainability.
“In our first conversations, Dr Doi proposed we build wooden housing on the Moon,” says staff member Koji Murata on the biomaterials-design laboratory at Kyoto College’s Graduate Faculty of Agriculture. “We have also discussed the possibility of building domes on Mars out of wood in order to grow timber forests.”
Martian and lunar colonists, like all pioneers, must make use of native supplies — regolith (rocky materials on the floor), silicon dioxide and different minerals, within the case of Mars. However wooden might play an element in crafting non permanent or everlasting shelters. Murata factors to plans by JAXA and industrial companions to develop shelters made partly of wooden that might be utilized in Antarctica or on the Moon.
“The natural radiation-shielding properties of wood could be used effectively to design walls or outer shells of space habitats to provide protection,” says Nisa Salim, who makes a speciality of engineered supplies at Swinburne College of Expertise in Melbourne, Australia, and isn’t a part of the mission. “Wood is an effective insulator, capable of regulating temperature and minimizing heat transfer to maintain a comfortable indoor environment. Wood is easy to work with, renewable and biodegradable, aligning with sustainability goals for space exploration.”
Salim famous that the structural integrity, security and longevity of wooden should be confirmed in area.
Wooden consists of cellulose held collectively by lignin, a sort of natural polymer. That makes it a naturally occurring member of the category of supplies often called composites, says Scott J McCormack, a supplies engineer on the College of California, Davis, who shouldn’t be concerned within the mission. Composites are sometimes used within the aerospace business, so he doesn’t discover it shocking that their use in satellites is perhaps explored.
“Composites are ideal for the aerospace industry — and also satellites — due to their high strength-to-weight ratio,” says McCormack. However he has doubts about how wooden will fare as a structural materials on the Moon or Mars. “The first concern that comes to mind is galactic cosmic radiation [GCR] and how it might degrade the mechanical properties of wood over time. GCR isn’t that big of problem for us here on Earth, thanks to our atmosphere.”
However Murata says that the staff has studied measurements of GCR and photo voltaic energetic particles — high-energy particles which are launched from the Solar — taken by NASA’s Curiosity rover on Mars, in addition to the consequences of gamma rays on wooden on Earth. He thinks that wooden on Mars might probably final for hundreds of years. “Radiation on Mars is a big problem for living organisms, including humans,” he says. “I don’t think this is going to be much of an issue for wood.”
This text is reproduced with permission and was first revealed on June 7, 2024.

