The primary ice-free day within the Arctic Ocean may arrive as quickly as this decade, warns a brand new examine.
Climatologists from Colorado College (CU) Boulder and the College of Gothenburg have used pc fashions to research when the Arctic may expertise its first ice-free day. On this context, ‘ice-free’ means a sea ice space of 1 million sq. kilometers (386,000 sq. miles) or much less.
The staff used 11 totally different local weather fashions to run 366 simulations of local weather change from 2023 to 2100. They discovered that the primary ice-free day within the Arctic appeared throughout fairly a variety of prospects: it may happen in as little as three years, or it may not occur by the tip of the century.
Nonetheless, the vast majority of simulations predicted that this fateful day would arrive inside 7 to twenty years. That was the case even when people decreased their greenhouse gasoline emissions – which we’re doing a horrible job of thus far.
9 of the simulations reached an ice-free day inside three to 6 years. This situation is unlikely however poses a excessive danger, so the researchers investigated the circumstances that led to such a fast transition.
All it could take is an unusually heat fall, winter, and spring, which primes the next summer time to soften extra sea ice. If this sample holds for 3 consecutive years, the primary ice-free day would happen by September of a given 12 months.
An ice-free day would not be a one-off occasion both. Extra would in fact observe, finally culminating in complete months under the ice-free threshold.
“The first ice-free day in the Arctic won’t change things dramatically,” says Alexandra Jahn, CU Boulder climatologist.
“But it will show that we’ve fundamentally altered one of the defining characteristics of the natural environment in the Arctic Ocean, which is that it is covered by sea ice and snow year-round, through greenhouse gas emissions.”
The quantity of sea ice within the Arctic and Antarctic naturally shrinks and grows all through the course of the 12 months. The utmost and minimal extents have been monitored since November 1978 to trace the consequences of local weather change.
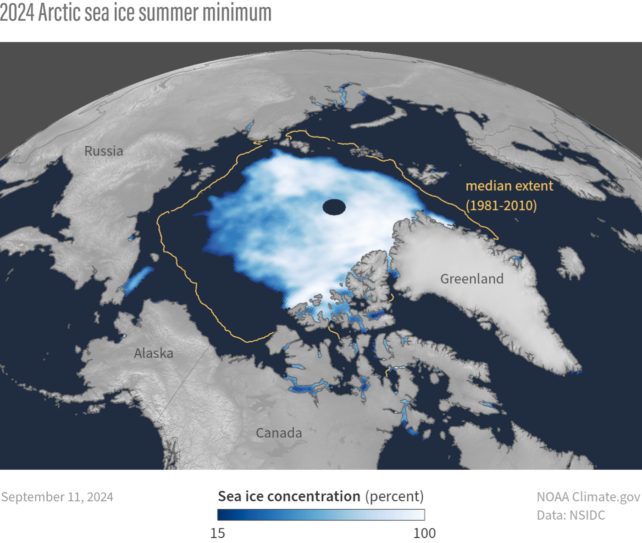
This 12 months, for instance, the minimal sea ice space was recorded on September 11, at 4.28 million sq. kilometers. That makes it the seventh smallest space on document, with the loss exhibiting a downward pattern of 12.4 % per decade.
Projecting forwards, scientists have beforehand estimated when the Arctic may turn out to be ice-free for giant chunks of its summertime. For the new examine, the researchers investigated an missed stepping stone on that path: when the primary ice-free day may happen.
In all 9 of the worst-case situation simulations, sea ice was preconditioned for a number of years earlier than the primary ice-free day occurred. In these years, atmospheric cooling arrives later in autumn, and heat spells seem as late as December.
In the course of the ‘closing’ winter earlier than, temperatures linger above -20 °C (-4 °F) for prolonged intervals, lowering the quantity of latest ice fashioned.
Spring could arrive as much as one month sooner than normal, or see fewer chilly spells. Heatwaves of over 0 °C turn out to be widespread. And eventually, the summer time that includes that fateful day could be very heat, with temperatures over 10 °C. Storms at the moment can additional stress sea ice.

Collectively, these circumstances can set off the primary ice-free day to reach in August or September. After that first day, the Arctic stays ice-free for between 11 and 53 days in these 9 fast transition simulations.
The researchers aren’t investigating this simply to bum individuals out. The examine discovered that ice-free days in all fast transition circumstances occurred in years the place international warming exceeded 1.5 °C above the pre-industrial baseline – the goal of the Paris Settlement.
If nations can follow the rules set out in that settlement, an ice-free Arctic might be delayed, the staff says. Sadly, 2024 is on monitor to be the first 12 months above 1.5 °C of warming, so we is likely to be heading down a adverse path sooner slightly than later.
The analysis was printed within the journal Nature Communications.

