In September 1933, American meteorologist Joseph Kincer requested a easy query: is the local weather altering? So started the trouble to know the scope of humanity’s interference with the local weather.
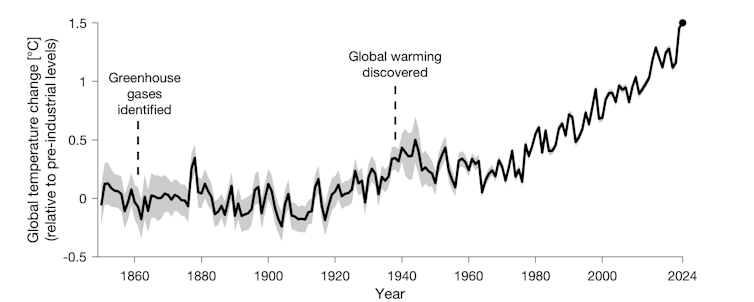
By analyzing tendencies in measured temperatures at many various places all over the world, Kincer concluded that the world was getting hotter, however didn’t counsel a purpose. A number of years later in 1938, British engineer Man Callendar confirmed that Earth’s land temperatures had warmed by about 0.3°C within the earlier 50 years.
Callendar additionally argued that this warming was largely resulting from elevated ranges of carbon dioxide within the ambiance from the burning of coal, which constructed on earlier theories of the greenhouse impact.
Right now, measurements from hundreds of climate stations on land and from satellites and ships are mixed with climate forecast fashions to supply a constant image of how the local weather is altering day-to-day and decade to decade.
Negotiators are gathered in Azerbaijan for Cop29 (the newest spherical of UN local weather change negotiations) at a time of nice peril. The final two years, 2023 and 2024, had been the warmest in information stretching again to the mid-Nineteenth century and will probably be near 1.5°C above the temperature of the early industrial period.
It took a century for the globe to heat the primary 0.3°C, however the world has warmed by 1°C in simply the final 60 years.
Earth is getting hotter, and at a quicker charge.
Charge of warming
What determines the speed of world warming now could be primarily humanity’s emissions of greenhouse gases. If the quantity of greenhouse fuel we’re emitting will increase, then the speed at which the world is getting hotter quickens. Cut back emissions and warming continues, however at a slower tempo. Solely as soon as emissions are internet zero are world temperatures anticipated to roughly stabilise.
There are different elements and, consequently, the globe has not warmed on the similar charge by time. The speed of world warming has been pretty even at 0.2°C per decade from 1970 till now, a lot quicker than any interval earlier than. The final two years may counsel the speed is accelerating, although this isn’t but clear.
Earlier than 1970 there was a interval of slight world cooling resulting from a fast enhance in reflective aerosol particles being added to the ambiance, additionally resulting from burning fossil fuels.
The onset of fresh air insurance policies launched within the Sixties in lots of western international locations lowered this cooling affect. Earlier than the second world warfare, pure variations within the local weather dominated, with a really gradual warming affect from early industrialisation.
Nor has the world warmed equally in every single place. Land has sometimes warmed quicker than the worldwide common, with ocean areas warming extra slowly. The Arctic is warming quickest of all at as much as 4 instances the worldwide common.
What’s the outlook for 2025? Persistent heat over the past two years has barely shocked local weather scientists. However it’s extra possible than not that 2025 will probably be cooler than 2024, given the transition to La Niña situations within the tropical Pacific Ocean. That is the cool section of a pure cycle often called El Niño Southern Oscillation, or Enso.
And past? We are going to exceed 1.5°C of warming as a long-term common someday within the subsequent decade or so. Our selections within the subsequent few years will decide whether or not we will restrict world warming to 1.6°C or 1.7°C above pre-industrial ranges, or whether or not the world will proceed to heat, with extra critical penalties the upper temperatures get.![]()
Ed Hawkins, Professor of Local weather Science, College of Studying
This text is republished from The Dialog underneath a Artistic Commons license. Learn the unique article.

