This experiment aimed to extract DNA from cheek cells and decide the size of an unknown DNA fragment utilizing gel electrophoresis. The DNA was extracted by swishing Gatorade within the mouth, adopted by mixing with detergent, pineapple juice, and isopropyl alcohol, which precipitated the DNA. The extracted DNA was visualized on the interface of the alcohol and resolution. For gel electrophoresis, DNA samples, together with a dye combination, unknown DNA, and DNA markers, had been loaded into an agarose gel, and an electrical subject was utilized to separate the fragments by dimension. The space migrated by the DNA markers allowed for the estimation of the unknown DNA fragment’s size. The outcomes confirmed that the unknown DNA fragment was roughly 2.7 kilobases (kb) lengthy, primarily based on the semi-logarithmic normal curve. This experiment efficiently demonstrated DNA extraction and electrophoresis, offering insights into molecular biology methods for DNA evaluation.
Gel electrophoresis separates DNA, RNA, or proteins by dimension (Hames et.al, 1990). Every DNA molecule is a double helix made up of two complementary nucleotide strands held collectively by hydrogen bonds between the bottom pairs guanine (G)-cytosine (C) and adenine (A)-thymine (T). DNA consists of negatively charged phosphate spine causes migration towards the optimistic electrode beneath an electrical subject (Alberts et. al, 2002). Dyes like ethidium bromide and SmartGlow Pre Stain (a non-carcinogenic different) visualize DNA by fluorescing beneath UV gentle. Molecules transfer via the gel’s pores at charges inversely proportional to their size; smaller fragments migrate sooner (Mika et. al, 2024).
Agarose gels are primarily utilized in gel electrophoresis, the place an electrical subject is utilized to separate biomolecules primarily based on their dimension and cost. The gel matrix acts as a molecular sieve, permitting smaller molecules emigrate sooner than bigger ones. Agarose gel is a gel-like substance derived from agar; a polysaccharide obtained from crimson algae. It’s extensively utilized in molecular biology for the separation and evaluation of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) and proteins. Gel focus impacts pore dimension and resolving energy, and migration distances could be plotted towards the logarithm of molecular size. DNA markers or ladders, containing identified fragment sizes, enable for correct dimension estimation of unknown samples by evaluating migration distances. By creating an ordinary curve from known-length molecules, the lengths of unknown DNA could be calculated, sometimes expressed in kilobases (kb) or base pairs (bp) (Lee et. al, 2012).
The target of this experiment is to measure the size of an unknown DNA fragment by analyzing its electrophoretic migration compared to normal DNA fragments of identified lengths.
If the unknown DNA fragment migrates equally to an ordinary DNA fragment of identified size, then its dimension could be estimated primarily based on that comparability.
DNA Extraction from Cheek Cells
DNA extraction from cheek cells concerned swishing 5 ml of Gatorade of their mouth for two minutes, then transferring the answer to a take a look at tube. After including 2 ml of dishwashing detergent and swirling the tubes to combine, 2 ml of pineapple juice was added to the answer. The tubes had been inverted to combine. Subsequent, 2 ml of ice-cold isopropyl alcohol was gently added, and the tube was left for 10 minutes to precipitate the DNA (Mika et al., 2024).
Preparation of Agarose gel
For the following experiment, Agarose gels had been ready prematurely and saved with the grey plastic comb in place. This comb was rigorously eliminated after the gel solidified and saved for reuse. Every scholar was assigned a selected gel and electrophoresis unit, with the chamber designed to accommodate one gel. When loading samples, it was suggested to skip the top wells to stop contamination, and college students had been inspired to load two samples of every DNA kind if desired.
Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
Every gel was loaded with three kinds of samples: a dye combination, unknown DNA, and a DNA marker, with every nicely holding roughly 25 µL of pattern.
The DNA samples had been ready and frozen previous to the experiment. To load the samples, a micropipette outfitted with a disposable pipet tip was used. The tip was submerged within the pattern resolution, and by urgent the thumb button, 25 µL of the pattern was drawn into the pipet tip. Care was taken to examine for and expel any air bubbles earlier than rigorously directing the pipet tip into the submerged nicely of the gel. Every nicely was stuffed to its 25 µL capability with out overfilling, and a brand new pipet tip was used for every pattern to keep away from cross-contamination. After loading, the pattern vials had been returned to the freezer.
As soon as the DNA samples had been loaded, the gels had been positioned within the electrophoresis chamber with the wells closest to the black (adverse) electrode, guaranteeing that DNA would migrate towards the crimson (optimistic) electrode. The buffer resolution (0.04 M Tris-Acetate EDTA, pH 8.0) was ready and chilled prematurely, and roughly 200 mL of this chilly buffer was added to cowl the gels fully, eliminating any trapped air bubbles. The orange lid was positioned gently on high, adjusting as mandatory.
An 8 cm clear ruler was positioned on the lid, aligned with the wells to observe DNA migration visually. The gel electrophoresis unit was then linked to an influence supply, and the settings had been adjusted to run at 100 volts for 35 minutes. The timer was set, and the beginning button was pressed as soon as all parameters had been confirmed. The progress of DNA migration was noticed by turning on the blue LED gentle beneath the chamber, which illuminated the bands as they moved away from the wells.
Electrophoresis continued till the dye combination had migrated to inside 2-3 mm of the gel’s finish. After the run, the unit was turned off, and the cables had been disconnected. The gels had been visualized beneath the blue LED gentle, and pictures had been taken utilizing a black imaging field with an orange filter taped to the lid. Care was taken to align the digital camera with the ruler for correct measurement of bands.
Information Evaluation
Following imaging, the gap migrated by DNA Marker Fragment was measured in mm utilizing ruler. Outcomes had been recorded in a chosen desk for evaluation. This distance was plotted on a semi-logarithmic graph towards the identified sizes of the DNA markers to estimate the unknown fragment’s size in kilobases (kb). The space migrated by the unknown DNA fragment was measured from the nicely to the forefront of the band. Utilizing the usual curve, the corresponding worth on x-axis of graph, which is the size of unknown DNA fragment (Mika et al., 2024).
Simplified protocol
DNA Extraction from Cheek Cells:
- Swish 5 mL of Gatorade in mouth for two minutes.
- Switch the answer to a take a look at tube.
- Add 2 mL of dishwashing detergent and swirl to combine.
- Add 2 mL of pineapple juice and invert the tube to combine.
- Gently add 2 mL of ice-cold isopropyl alcohol.
- Depart the tube for 10 minutes to precipitate the DNA.
Agarose Gel Electrophoresis:
- Put together agarose gels prematurely, storing them with a grey plastic comb.
- Take away the comb rigorously after the gel solidifies for reuse.
- Assign particular gels and electrophoresis models to every scholar.
- Skip finish wells to keep away from contamination when loading samples.
- Load three kinds of samples into the wells: dye combination, unknown DNA, and DNA marker (25 µL per nicely).
- Put together and freeze DNA samples previous to the experiment.
- Use a micropipette with a disposable pipet tip to load samples into the wells.
- Guarantee no air bubbles within the pipette tip and use a brand new tip for every pattern.
- Make sure the gel is positioned within the electrophoresis chamber with the wells close to the black (adverse) electrode.
- Put together and chill 200 mL of buffer resolution (0.04 M Tris-Acetate EDTA, pH 8.0) prematurely.
- Add the chilled buffer to cowl the gels fully, eradicating air bubbles.
- Place the orange lid on the electrophoresis chamber, adjusting if mandatory.
- Use an 8 cm clear ruler to observe DNA migration visually, aligned with the wells.
- Set the electrophoresis unit to 100 volts for 35 minutes.
- Observe the DNA migration utilizing the blue LED gentle beneath the chamber.
- Proceed electrophoresis till the dye combination is 2-3 mm from the top of the gel.
- After the run, flip off the unit and disconnect the cables.
- Visualize the gels beneath blue LED gentle and take images utilizing a black imaging field with an orange filter.
- Align the digital camera with the ruler for correct measurement of bands.
Information Evaluation:
- Measure the gap migrated by the DNA Marker Fragment in mm utilizing a ruler.
- File the measurements in a desk for evaluation.
- Plot the migration distance on a semi-logarithmic graph towards the identified DNA marker sizes.
- Estimate the size of the unknown DNA fragment in kilobases (kb) utilizing the usual curve.
Outcomes
The DNA extracted from cheek cells was efficiently precipitated and have become seen on the interface of the alcohol and the answer within the take a look at tube.
The space migrated by DNA marker fragment was measured. The distances had been plotted in a semi-log graph.
| DNA Marker Fragment Quantity | DNA Maker Fragment Size (KBP) | DNA Marker Fragment Distance Migrated (mm) |
| 1 | 23.13 | 18 |
| 2 | 9.41 | 25 |
| 3 | 6.68 | 30 |
| 4 | 4.36 | 38 |
| 5 | 2.32 | 58 |
| 6 | 2.03 | 63 |
Desk 1: DNA Marker Fragment Size
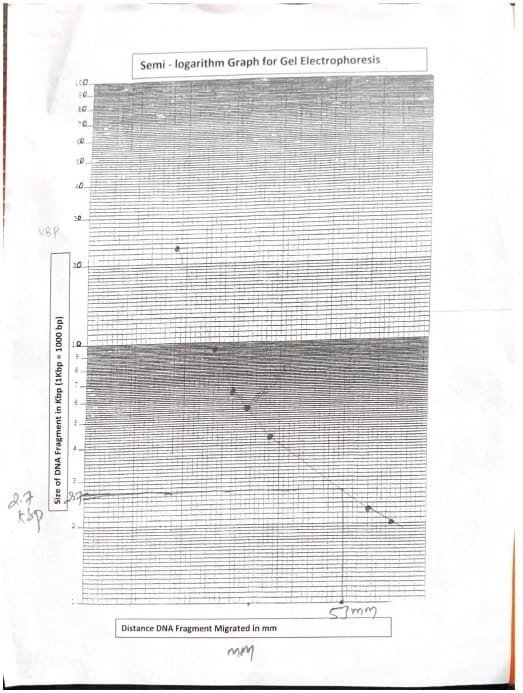
The space migrated by unknown DNA fragment was measured and the fragment size was recognized by evaluating with the corresponding worth of marker in semi-log paper.
| Unknown DNA Fragment Migrated (mm) | Unknown DNA Fragment Size (KBP) |
| 53mm | 2.7 KBP |
Desk 2: Unknown DNA Fragment Size Dedication
Dialogue
The DNA was extracted from cheek cells by including numerous options, which facilitated its precipitation and made it seen on the interface of the alcohol and the answer within the take a look at tube. DNA molecules are too small to be visualized and might solely be seen utilizing electron microscope, however clumping makes it seen (Mika et. al, 2024).
The gel electrophoresis experiment successfully demonstrated the separation of DNA fragments primarily based on dimension, using agarose gel because the medium (Hames et. al, 1990). The 0.04 M Tris-Acetate EDTA buffer at pH 8.0 facilitated the motion of negatively charged DNA towards the optimistic electrode (Alberts et. al, 2002). The constructed normal curve from identified DNA markers allowed us to estimate the unknown fragment’s size at roughly 2.7 kilobases (kb).
The distinct separation of the dye combination confirmed the integrity of the electrophoresis course of, indicating that the gel was functioning correctly. Visualization beneath blue gentle enabled clear imaging of DNA bands, and cautious alignment with a ruler ensured correct distance measurements.
General, this experiment efficiently illustrated the ideas of gel electrophoresis, emphasizing the significance of unpolluted pattern preparation and experimental circumstances for acquiring dependable outcomes. Future research might examine completely different agarose concentrations or incorporate further controls to reinforce the evaluation additional.
References
- Hames, B. D., & Rickwood, D. (1990). Gel Electrophoresis of Nucleic Acids: A Sensible Method. Oxford College Press.
- Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, et al. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 4th version. New York: Garland Science; 2002. The Construction and Operate of DNA. Out there from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK26821/
- Mika, T. A., Klein, R. J., Bullerjahn, A. E., Connour, R. L., Swimmer, L. M., White, R.
- E., Gosses, M. W., Carter, T. E., Andrews, A. M., Maier, J. L., & Sidiq, F. (Eds.). (2024). Anatomy and physiology BIO 211 laboratory handbook (third ed.). Owens Neighborhood Faculty.
- Lee, P. Y., Costumbrado, J., Hsu, C. Y., & Kim, Y. H. (2012). Agarose gel electrophoresis for the separation of DNA fragments. Journal of visualized experiments : JoVE, (62), 3923. https://doi.org/10.3791/3923

