Again in 2021, a take a look at of cephalopod smarts strengthened how vital it’s for us people to not underestimate animal intelligence.
Cuttlefish got a brand new model of the marshmallow take a look at, and the outcomes might reveal that there is extra occurring of their unusual little brains than we knew.
Their potential to be taught and adapt, the researchers stated, might have developed to present cuttlefish an edge within the cutthroat eat-or-be-eaten marine world they dwell in.
The marshmallow take a look at, or Stanford marshmallow experiment, is fairly easy.
A baby is positioned in a room with a marshmallow. They’re advised if they’ll handle to not eat the marshmallow for quarter-hour, they’re going to get a second marshmallow, and be allowed to eat each.
This potential to delay gratification demonstrates cognitive talents equivalent to future planning, and it was initially carried out to review how human cognition develops; particularly, at what age a human is sensible sufficient to delay gratification if it means a greater final result later.
As a result of it is so easy, it may be adjusted for animals. Clearly you’ll be able to’t inform an animal they’re going to get a greater reward in the event that they wait, however you’ll be able to practice them to grasp that higher meals is coming if they do not eat the meals in entrance of them right away.
Some primates can delay gratification, together with canine, albeit inconsistently. Corvids, too, have handed the marshmallow take a look at.
In 2020, cuttlefish additionally handed a model of the marshmallow take a look at. Scientists confirmed that widespread cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis) can chorus from consuming a meal of crab meat within the morning as soon as they’ve learnt dinner will likely be one thing they like a lot better – shrimp.
Nevertheless, as a workforce of researchers led by behavioral ecologist Alexandra Schnell of the College of Cambridge identified, on this case it was tough to find out whether or not this modification in foraging habits in response to prey availability was additionally being ruled by a capability to exert self-control.
In order that they designed one other take a look at, for six widespread cuttlefish. The cuttlefish had been positioned in a particular tank with two enclosed chambers that had clear doorways so the animals might see inside. Within the chambers had been snacks – a less-preferred piece of uncooked king prawn in a single, and a way more attractive dwell grass shrimp within the different.
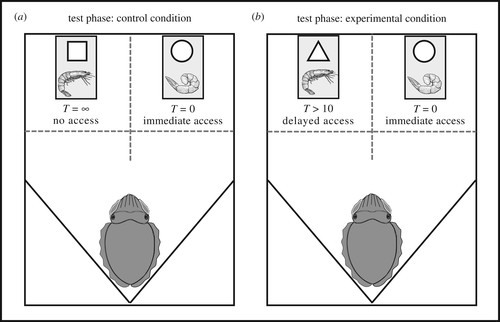
The doorways additionally had symbols on them that the cuttlefish had been skilled to recognise. A circle meant the door would open right away. A triangle meant the door would open after a time interval between 10 and 130 seconds. And a sq., used solely within the management situation, meant the door stayed closed indefinitely.
Within the take a look at situation, the prawn was positioned behind the open door, whereas the dwell shrimp was solely accessible after a delay. If the cuttlefish went for the prawn, the shrimp was instantly eliminated.
In the meantime, within the management group, the shrimp remained inaccessible behind the square-symbol door that would not open.
The researchers discovered that the entire cuttlefish within the take a look at situation determined to attend for his or her most popular meals (the dwell shrimp), however did not trouble to take action within the management group, the place they could not entry it.
“Cuttlefish in the present study were all able to wait for the better reward and tolerated delays for up to 50-130 seconds, which is comparable to what we see in large-brained vertebrates such as chimpanzees, crows, and parrots,” Schnell stated again in 2021.
The opposite a part of the experiment was to check how good the six cuttlefish had been at studying. They had been proven two completely different visible cues, a gray sq. and a white one.
After they approached one, the opposite can be faraway from the tank; in the event that they made the “correct” selection, they’d be rewarded with a snack.
As soon as they’d learnt to affiliate a sq. with a reward, the researchers switched the cues, in order that the opposite sq. now grew to become the reward cue.
Apparently, the cuttlefish that learnt to adapt to this modification the quickest had been additionally the cuttlefish that had been capable of wait longer for the shrimp reward.
That looks like cuttlefish can exert self-control, all proper, however what’s not clear is why.
In species equivalent to parrots, primates, and corvids, delayed gratification has been linked to components equivalent to software use (as a result of it requires planning forward), meals caching (for apparent causes) and social competence (as a result of prosocial habits – equivalent to ensuring everybody has meals – advantages social species).
Cuttlefish, so far as we all know, do not use instruments or cache meals, nor are they particularly social. The researchers suppose this potential to delay gratification might as a substitute have one thing to do with the best way cuttlefish forage for his or her meals.
“Cuttlefish spend most of their time camouflaging, sitting and waiting, punctuated by brief periods of foraging,” Schnell stated on the time.
“They break camouflage when they forage, so they are exposed to every predator in the ocean that wants to eat them. We speculate that delayed gratification may have evolved as a byproduct of this, so the cuttlefish can optimize foraging by waiting to choose better quality food.”
It is an interesting instance of how very completely different existence in very completely different species may end up in comparable behaviors and cognitive talents.
Proof of “episodic-like reminiscence” has been present in cuttlefish, and in 2024 scientists reported the primary statement of the creature forming false recollections.
Future analysis ought to, the workforce famous, attempt to decide if certainly cuttlefish are able to planning for the longer term.
The workforce’s analysis was revealed in Proceedings of the Royal Society B.
A model of this text was first revealed in March 2021.

