Suspended within the relic of an historic sea beneath southern Arkansas, there could also be sufficient lithium for 9 occasions the anticipated international demand for the factor in automotive batteries in 2030.
A collaborative nationwide and state authorities analysis staff educated a machine studying mannequin to foretell and map the lithium concentrations of salty water deep inside the porous limestone aquifer beneath southern Arkansas, often known as the Smackover Formation brines.
The mannequin was educated on current and new brine lithium knowledge from the area, factoring in identified variations in geology, geochemistry, and temperature.
The outcomes recommend there may be wherever from 5.1 to 19 million tons of lithium within the brines, which might account for 35–136 p.c of the present estimated lithium sources within the US.
And that would cut back dependence on lithium imports, one thing US Division of Vitality officers have their sights set on.
The research additionally signifies that in 2022, brines dropped at the floor by the oil, fuel, and bromine industries contained 5,000 tons of dissolved lithium – a useful resource that’s turning into more and more essential as we flip away from inner combustion engines pushed by fossil fuels, and in direction of battery-powered electrical and hybrid autos.
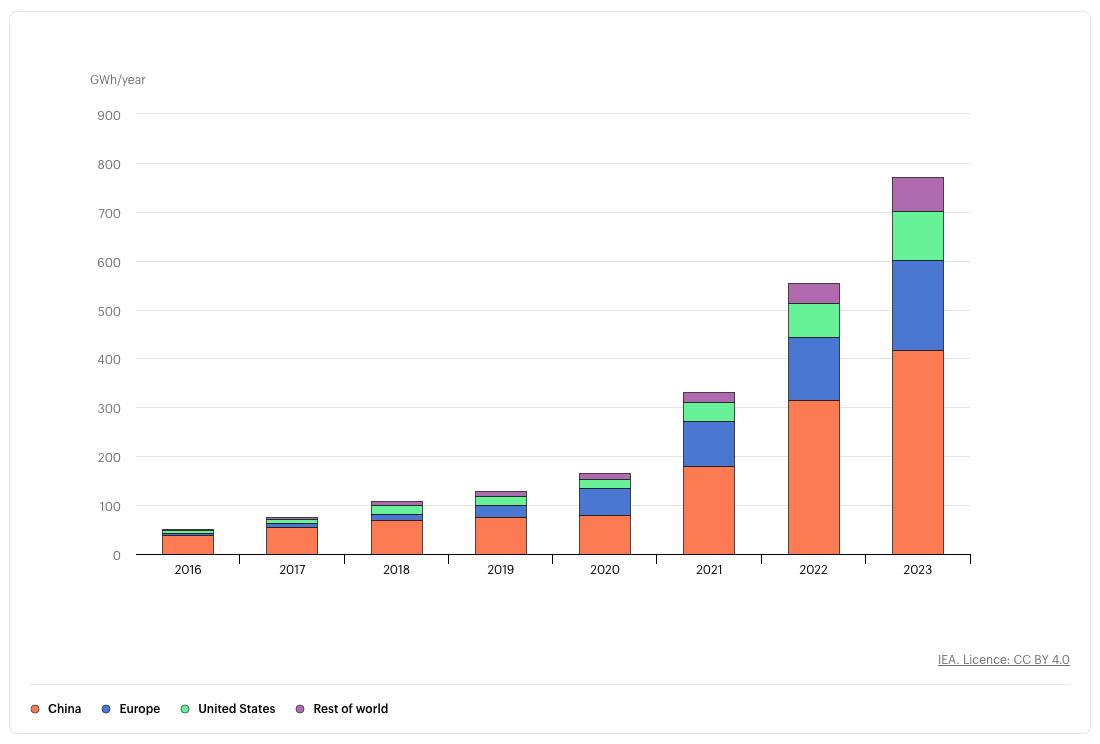
Lithium is the fabric of alternative for electrical automobile batteries, and demand for these is sharply rising. In keeping with the Worldwide Vitality Company (IEA), electrical automobile batteries accounted for about 85 p.c of complete lithium demand in 2023, a rise of 30 p.c from 2022.
“Mining and refining will need to continue growing quickly to meet future demand,” the IEA reviews.
However any point out of recent mining and groundwater extraction can and most likely ought to elevate an eyebrow.
Different types of lithium mining contain strip mines – which decimate every little thing above floor together with the deeper layers, and evaporation ponds – which produce solely small quantities of lithium at a value of huge quantities of water, together with clouds of poisonous mud.
In south Arkansas, however, the bromine trade already makes use of a course of through which brine is pumped out of the aquifer, bromine is extracted, after which the ensuing wastewater is pumped again down.
Lithium is, doubtlessly, simply an additional mineral to be salvaged within the course of – and the researchers suspect this implies lithium sources have not but been depleted by current mining, both.
However this course of would not assure zero environmental affect; slightly, it is a main unknown one. And numerous corporations are lining as much as drill new wells.
Patrick Donnelly, a conservation biologist and the Nice Basin director for the Middle of Organic Variety, informed Jack Travis from Ozarks at Massive:
“We are in favor of electric vehicles and battery storage as a part of the transition off of fossil fuels… [but] we are sort of actively searching for where is lithium production in the United States that is not going to harm communities and the environment.”
“There is no such thing as a free lunch. And there are impacts from [direct lithium extraction],” he says.
Little doubt this can be a tough stability to strike, however this new analysis could possibly be used to assist get it proper.
“Lithium is a critical mineral for the energy transition, and the potential for increased US production to replace imports has implications for employment, manufacturing and supply-chain resilience,” US Geological Survey director David Applegate says.
“This study illustrates the value of science in addressing economically important issues.”
This analysis was revealed in Science Advances.

