The abyssal depths of the world’s oceans are a spot of eerie thriller. The creatures that lurk therein reside unusual lives, vastly totally different from these on the temperate floor.
An encounter with one such creature was documented final yr. Deep beneath the Pacific Ocean, marine scientists recorded a sight not often seen by people: an octopus billowy-bouncing throughout the seafloor at a depth of 4,800 meters (15,750 ft) – smack bang within the abyssal zone.
The expedition was the Trans-Pacific Transit, and researchers from the College of Western Australia aboard the vessel Dagon used submerged laboratories to peek on the life that thrives within the freezing chilly temperatures, crushing pressures, and everlasting darkness far under the ocean waves.
Their video reveals an octopus referred to as a big-eye jellyhead (Cirrothauma cf. magna).
frameborder=”0″ allow=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share” referrerpolicy=”strict-origin-when-cross-origin” allowfullscreen>
We do not know a lot about this octopus; the place it lives is extraordinarily tough for people to discover, so we do not precisely get to watch it in its pure abyssopelagic habitat regularly.
A 1997 research presents some clues concerning the unusual boinging. It describes observations of cirrate octopuses bouncing alongside the seafloor in the identical vogue, and refers to it as a type of locomotion.
There is a diagram, and it is pleasant.
However there may very well be a bit extra to it. We have additionally seen associated cirrate octopuses hopping alongside the ocean ground in a similar way at shallower depths, which may very well be one other clue about what the heck this bouncy lil ocky is doing.
In a paper printed final yr in Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Organic Sciences, marine scientist Alexey Golikov of the GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Analysis in Germany and his colleagues described a bouncing foraging conduct noticed within the cirrate octopus referred to as the big-finned jellyhead (Cirroteuthis muelleri).
There’s one other diagram:
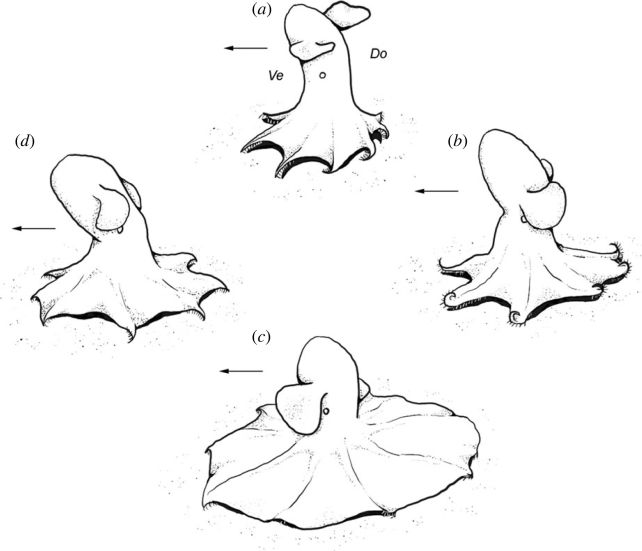
This octopus, the researchers described, performs the identical sequence as noticed within the current video of the big-eye jellyhead.
It bounces itself up off the seafloor; on the apex of every bounce, it spreads its arms, ballooning out the membrane between them to land on the seafloor. Throughout this landing, the octopus captures any prey that it managed to embody, earlier than bouncing up once more and repeating the sequence.
The observations, obtained between 2020 and 2022, marked the primary time this feeding conduct had been seen and documented in cirrate octopuses.
There may be a lot we do not learn about life in Earth’s oceans. However one factor is turning into abundantly clear: even on the deepest, darkest, coldest depths of the ocean, unimaginable ecosystems are discovering a technique to thrive.
Life finds a means – even it is a surprisingly boinging balloony one.

