Scientists have taken a significant step in direction of discovering elusive sorts of tiny, ‘ghost-like’ particles, and probably new physics.
For the primary time, neutrinos have been noticed by the Quick-Baseline Close to Detector (SBND) on the Fermi Nationwide Accelerator Laboratory (Fermilab).
It is a important second within the decades-long quest so as to add to what we find out about a few of the most plentiful particles within the Universe.
With such tiny plenty and solely the slimmest of possibilities of interacting with different particles, 100 trillion of them move via our our bodies every second with out us being any the wiser. But their properties are so distinctive, their very existence might assist clarify why we have now a Universe of atoms, molecules, stars, and galaxies.
We already find out about three sorts of neutrinos – muon, electron, and tau – however some experiments counsel there’s one other one ready to be discovered, a so-called ‘sterile’ kind that’s much more ghost-like than the remaining. Confirming its existence is likely one of the key jobs of the newly operational SBND.
“We think neutrinos could help us get at some huge questions, like finding a more complete theory of nature at the smallest scales, or even why our matter-filled Universe exists at all,” says experimental particle physicist Andrew Mastbaum, from the Rutgers College of Arts and Sciences in New Jersey.
Work on the SBND has been happening for nearly a decade, so the looks of the primary neutrino reactions has been a very long time coming. It is full of 112 tons of tremendous chilled liquid argon that may detect the fleeting brush of a neutrino’s interplay by way of the weak nuclear power.
Different detectors across the globe, similar to Antarctica’s IceCube Neutrino Observatory, try to snare the numerous neutrinos showering down from cosmic reactions. Experiments right here on Earth additionally churn out neutrinos in processes we have now significantly better management over, making it invaluable that we detect these particles as effectively.
The SBND goes to affix up with the ICARUS (Imaging Cosmic And Uncommon Underground Alerts) machine, put in in 2017 and round 500 meters (or a 3rd of a mile) away. Collectively, they will analyze the particle accelerator beams generated from Fermilab.
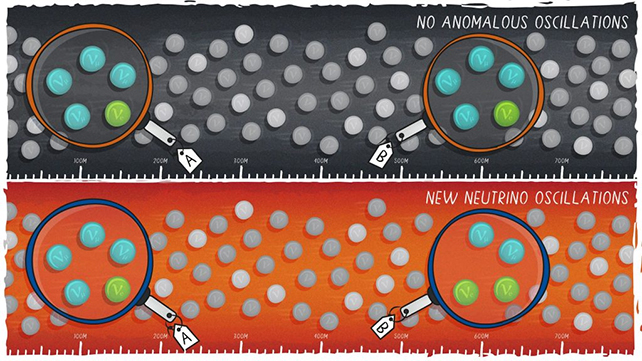
As many as round 7,000 neutrino interactions could possibly be detected per day – an enormous quantity contemplating how uncommon these interactions often are. The 2 detectors can then look ahead to traces from the collisions, and simply possibly, spot one thing that appears like a brand new variation on the neutrino.
“Detecting the photons produced by the beam helps us determine the start time and duration of the particle interactions,” says physicist Richard Van de Water, from Los Alamos Nationwide Laboratory in New Mexico.
“That information complements the tracking of particles produced in these interactions, giving us a fuller picture of the particle physics occurring.”
With SBND in a position to examine neutrinos with higher precision than ever earlier than, it is hoped that it would spot different patterns and anomalies that fall exterior the Commonplace Mannequin of physics, together with probably darkish matter. Do not be shocked to listen to extra from Fermilab, the SBND and ICARUS within the coming years, as operations scale up.
“Understanding the anomalies seen by previous experiments has been a major goal in the field for the last 25 years,” says physicist David Schmitz, from the College of Chicago.
“Together SBND and ICARUS will have outstanding ability to test the existence of these new neutrinos.”

