The microbial ecosystem nesting in your mouth is giving scientists a uncommon device to study how micro organism multiply.
One of the vital widespread micro organism dwelling in your dental plaque, a filamentous bacterium referred to as Corynebacterium matruchotii, divides not into two daughter cells like most cell divisions however a number of new microbes in a rarer course of referred to as a number of fission.
Led by microbiologist Scott Chimileski of the Marine Organic Laboratory within the US, a workforce of scientists noticed single C. matruchotii cells dividing up into as much as 14 new cells – a feat that may inform us how these organisms type the scaffolding that helps the hosts of different microbes which might be dwelling in your mouth.
“Reefs have coral, forests have trees, and the dental plaque in our mouths has Corynebacterium,” explains microbiologist Jessica Mark Welch of ADA Forsyth Institute and the Marine Organic Laboratory.
“The Corynebacterium cells in dental plaque are like a big, bushy tree in the forest; they create a spatial structure that provides the habitat for many other species of bacteria around them.”
Most micro organism and archaea reproduce through an asexual course of referred to as binary fission. The nucleus of the only cell that constitutes the organism splits into two nuclei; then the cell itself divides, leading to two organisms the place there was one.
Welch and her colleagues grew to become considering the way in which C. matruchotii propagates after conducting a earlier research into the way in which colonies of plaque micro organism arrange themselves spatially within the biofilm that coats human enamel. The plaque microbiome kinds a type of spiky ‘hedgehog’ construction, with filaments of C. matruchotii as a base.
To look at how these constructions add new filaments, the researchers used time-lapse microscopy, observing in real-time how the micro organism inside the microbiome work together with one another, coexist, propagate, and develop.
That is the place they noticed the bizarre cell division of C. matruchotii was not the conventional binary type, however far more prolific. And it does so in a really unusual method.
First, the filament elongates at only one finish, rising for much longer than the same old dimension of the cell. It does so at a fee 5 occasions quicker than different, carefully associated Corynebacterium species that dwell within the nostril or on the pores and skin.
Then, numerous dividing partitions referred to as septa type concurrently, earlier than the cell breaks aside into between 3 and 14 full daughter cells.
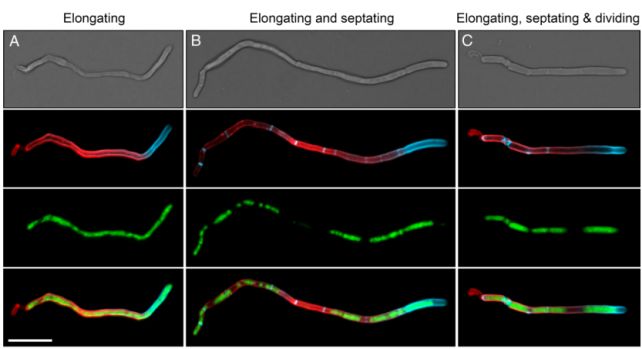
Because of this unusual course of, a colony of C. matruchotii can develop very quick certainly, as much as half a millimeter per day – which could assist clarify why plaque begins to return to your enamel inside hours, irrespective of how strenuously you clear them.
“These biofilms are like microscopic rainforests. The bacteria in these biofilms interact as they grow and divide. We think that the unusual C. matruchotii cell cycle enables this species to form these very dense networks at the core of the biofilm,” Chimileski says.
“Something about this very dense, competitive habitat of the dental plaque may have driven the evolution of this way of growing.”
frameborder=”0″ allow=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share” referrerpolicy=”strict-origin-when-cross-origin” allowfullscreen>
One other attention-grabbing factor about C. matruchotii which may drive its unusual development and division is that it lacks a flagellum; the whip-like appendage different micro organism use to get round. As a result of it’s fastened in place, its quick development could possibly be a method of exploring its surroundings and on the lookout for sources of meals, the researchers say.
It could possibly be how the microbe beneficial properties a aggressive benefit within the bacteria-crowded surroundings of the human mouth. However we have by no means seen something fairly prefer it. It is a completely new method for micro organism to thrive – and it has been proper right here, all alongside, in our personal our bodies.
“We propose that rapid growth by tip extension and simultaneous multiple division explain how C. matruchotii outcompetes other taxa to form filamentous networks at the core of the dental plaque biofilm,” the researchers write of their paper.
“Our findings extend beyond the oral microbiome, revealing a unique bacterial cell cycle and an example of how cell morphology and reproductive strategy can influence the spatial organization of microbial communities.”
The findings have been revealed within the Proceedings of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences.

