Innate immunity is the physique’s first line of protection in opposition to pathogens, offering fast, non-specific safety in opposition to a broad vary of invaders. Not like adaptive immunity, which targets particular pathogens with tailor-made responses, innate immunity acts shortly and uniformly upon encountering threats. This complete protection system contains numerous exterior boundaries, such because the pores and skin and mucous membranes, and inner mechanisms like phagocytic cells, acute-phase reactants, and inflammatory responses. By understanding the important thing traits and features of innate immunity, we achieve beneficial insights into how our physique combats infections and maintains well being from the very first level of contact with dangerous brokers.
Understanding Innate Immunity
1. Traits of Innate Immunity
- Broad Protection Mechanism: Innate immunity gives a non-specific protection in opposition to a variety of pathogens. It’s the physique’s preliminary response system, able to act instantly upon detecting an invader.
- No Want for Prior Publicity: The innate immune system doesn’t require prior publicity to a pathogen to mount a protection. That is in distinction to the adaptive immune system, which builds particular responses primarily based on earlier encounters with pathogens.
- Constant Response: The innate immune response is uniform, which means that it gives the same defensive response whatever the variety of exposures to a pathogen.
Exterior Protection System
The exterior protection system is the physique’s first line of protection in opposition to pathogens. It encompasses bodily, chemical, and organic boundaries designed to forestall infectious brokers from coming into the physique. Right here’s an in depth overview of those protecting mechanisms:
1. Bodily Obstacles
Pores and skin: The Main Barrier
- Construction and Operate: The pores and skin acts as a formidable bodily barrier to pathogen entry. It consists of two foremost layers:
- Dermis: The outermost layer consists of tightly packed epithelial cells lined in keratin, a tricky, protecting protein that helps stop pathogen penetration.
- Dermis: Positioned beneath the dermis, the dermis incorporates connective tissue, blood vessels, hair follicles, sebaceous glands, sweat glands, and white blood cells (WBCs). This layer helps the dermis and contributes to immune protection by way of its mobile and glandular elements.
- Secretions and Chemical Protection: The pores and skin’s secretions play an important position in discouraging microbial progress:
- pH Upkeep: The pores and skin’s floor is barely acidic, with a pH of roughly 5.6. This acidity is maintained by lactic acid and fatty acids secreted by sebaceous glands, creating an atmosphere that inhibits the expansion of many pathogens.
- Antibacterial Proteins: Proteins resembling psoriasin are current on the pores and skin and have antibacterial results. Psoriasin particularly targets Gram-negative micro organism like Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Gram-positive micro organism resembling Staphylococcus aureus, serving to to regulate bacterial colonization.
2. Mucous Membranes
Operate and Location
- Respiratory, Digestive, and Genitourinary Tracts: Mucous membranes line these tracts and function a bodily barrier to pathogens. They’re coated with mucus, a sticky substance that traps and helps to take away pathogens.
- Mucous Secretions: The mucus incorporates surfactants that stop micro organism from adhering to epithelial cells, lowering the danger of an infection.
3. Particular Protection Mechanisms in Numerous Tracts
Respiratory Tract
- Cilia: Tiny hair-like constructions referred to as cilia line the nasopharyngeal passages and assist to clear deposited particles and microorganisms.
- Reflex Actions: Coughing and sneezing are reflexes that expel pathogens from the respiratory tract, serving to to forestall their entry into the decrease respiratory system.
Digestive Tract
- Abdomen Acid: The abdomen secretes hydrochloric acid, making a extremely acidic atmosphere with a pH as little as 1. This acidity is efficient in killing most microorganisms that enter with meals or drink.
- Lysozyme: Present in tears and saliva, lysozyme is an enzyme that assaults the cell partitions of Gram-positive micro organism, contributing to the antimicrobial protection of the digestive tract.
Genitourinary Tract
- Urine: The method of urination helps to flush out pathogens from the urinary tract, lowering the probability of an infection.
- Vaginal pH: In females, the vaginal atmosphere is maintained at a pH of round 5 because of the presence of lactic acid. This acidic pH helps to inhibit the expansion of probably dangerous micro organism and yeast.
4. Microbiota (Regular Flora)
Position and Significance
- Aggressive Exclusion: The conventional flora, or microbiota, consists of assorted microorganisms that naturally reside on and inside the physique. These useful microbes compete with pathogenic organisms for assets and area, successfully stopping pathogens from establishing themselves.
- Immune System Assist: The microbiota additionally performs a job in modulating the immune response and sustaining total well being, making it a crucial element of the exterior protection system.
Inner Defenses
The inner protection system is essential for safeguarding the physique from pathogens that handle to bypass exterior boundaries. This method contains a wide range of mechanisms and cells that work collectively to determine, assault, and remove intruders. Right here’s a complete overview of the inner protection mechanisms:
1. Phagocytic Cells
Position and Operate
- Neutrophils: These are probably the most ample sort of white blood cells and infrequently the primary responders to an infection. Neutrophils phagocytose (engulf and digest) micro organism and different overseas particles. They’re notably efficient within the early levels of an infection and are a key element of the innate immune response.
- Macrophages: These cells are derived from monocytes and reside in tissues all through the physique. Macrophages are extremely versatile; they not solely engulf and destroy pathogens but in addition play an important position in presenting antigens to T cells, thus linking the innate and adaptive immune techniques. They assist to clear particles from lifeless cells and assist in tissue restore.
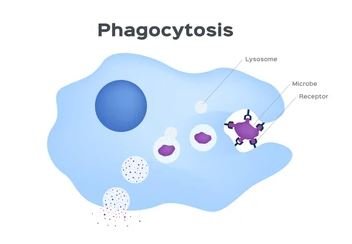
Mechanisms of Microbial Killing
- Oxygen-Dependent Mechanisms: After phagocytosis, neutrophils and macrophages generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) by way of processes just like the respiratory burst. ROS are extremely reactive molecules that destroy pathogens by damaging their mobile elements.
- Oxygen-Unbiased Mechanisms: These embody the usage of antimicrobial peptides, enzymes (e.g., lysozyme), and different molecules that may instantly kill or inhibit the expansion of pathogens with out the necessity for oxygen.
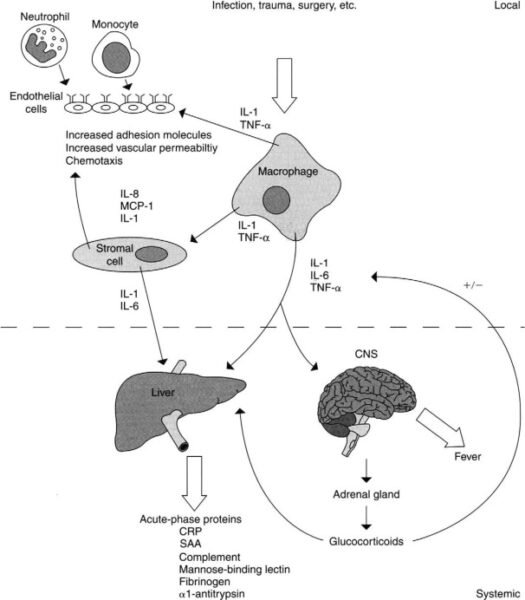
2. Acute-Part Reactants
Operate and Position
- C-Reactive Protein (CRP): One of many key acute-phase reactants, CRP ranges improve considerably in response to an infection, irritation, or damage. CRP binds to pathogens and broken cells, enhancing their recognition and phagocytosis by immune cells.
- Different Acute-Part Proteins: These embody serum amyloid A (SAA) and fibrinogen. These proteins assist to additional improve the inflammatory response, contribute to the clotting course of, and help the general immune protection.
3. Protecting Reflexes
Description and Operate
- Coughing and Sneezing: These reflex actions assist to expel pathogens from the respiratory tract. They’re triggered by irritation or the presence of overseas particles, and so they serve to clear the airways and cut back the danger of an infection.
- Vomiting and Diarrhea: Within the digestive tract, vomiting and diarrhea are mechanisms to expel ingested pathogens and toxins. Though uncomfortable, these processes assist to remove potential threats from the gastrointestinal system.
4. Inflammatory Response
Traits and Course of
- Vasodilation: Irritation begins with the dilation of blood vessels, which will increase blood stream to the affected space. This course of brings extra immune cells, vitamins, and oxygen to the positioning of an infection or damage.
- Elevated Vascular Permeability: The blood vessels develop into extra permeable, permitting immune cells and proteins to go by way of and enter the tissues. This helps to isolate and include the an infection.
- Immune Cell Migration: Neutrophils and macrophages migrate from the bloodstream to the positioning of an infection or injury. They carry out phagocytosis, engulfing and destroying pathogens, and in addition launch cytokines that assist regulate the immune response.
- Decision: After the risk is eradicated, the inflammatory response subsides, and therapeutic begins. Anti-inflammatory alerts are launched to restore the tissue and return the world to regular operate.
5. Sample Recognition Receptors (PRRs)
Operate
- Recognition of PAMPs: PRRs are specialised receptors on the floor of host cells that detect pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs). PAMPs are molecules distinctive to pathogens, resembling lipopolysaccharides on bacterial surfaces or viral RNA. By recognizing these patterns, PRRs allow the immune system to tell apart between self and non-self, initiating an applicable response.
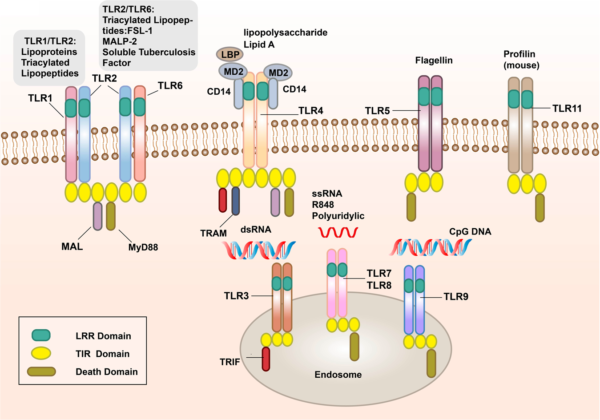
Varieties of PRRs and Their Capabilities
- Toll-Like Receptors (TLRs): TLRs are some of the well-characterized households of PRRs. They’re situated on the floor of immune cells and inside intracellular compartments. Every TLR is restricted to several types of PAMPs. For instance:
- TLR4 acknowledges LPS from Gram-negative micro organism.
- TLR3 detects double-stranded viral RNA.
- TLR5 binds to flagellin, a element of bacterial flagella.
- NOD-Like Receptors (NLRs): NLRs are cytoplasmic PRRs that acknowledge intracellular PAMPs. They play a job in detecting bacterial peptidoglycans and different pathogen-derived molecules contained in the cell. NLRs are concerned in initiating inflammatory responses and forming inflammasomes, that are multiprotein complexes that activate inflammatory cytokines.
- RIG-I-Like Receptors (RLRs): RLRs are cytoplasmic receptors that detect viral RNA. They’re essential for recognizing RNA viruses and initiating antiviral responses by way of the manufacturing of interferons and different cytokines.
- C-Sort Lectin Receptors (CLRs): CLRs acknowledge carbohydrate constructions on the surfaces of pathogens, resembling fungal cell partitions. They’re concerned within the recognition and phagocytosis of fungi and a few micro organism.
Activation and Response
- Sign Transduction: Upon recognition of PAMPs, PRRs activate intracellular signaling pathways that result in the manufacturing of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. These signaling pathways embody nuclear issue kappa B (NF-κB) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways, which drive the expression of genes concerned in irritation and immune responses.
- Inflammatory and Immune Response: The activation of PRRs results in an inflammatory response geared toward eliminating the pathogen. This contains the recruitment of extra immune cells to the positioning of an infection, the activation of antimicrobial mechanisms, and the initiation of restore processes.
What Are Innate Lymphoid Cells (ILCs)?
1. Overview of ILCs
- Origin and Improvement: Innate Lymphoid Cells (ILCs) originate from the widespread lymphoid progenitor (CLP) within the bone marrow. They don’t categorical the standard lymphoid markers discovered on B and T lymphocytes, which makes them distinct from different lymphoid cells.
- Main Areas: ILCs are predominantly situated at mucosal websites all through the physique, together with the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, and oral mucosa. These places are strategic as they’re the primary line of protection in opposition to environmental pathogens.
- Comparability with T Cells: Not like T cells, which possess particular antigen receptors for focused immune responses, ILCs lack these receptors. As a substitute, ILCs sense and reply to alerts from tissues which have been compromised by damage or an infection, offering a fast, generalized response.
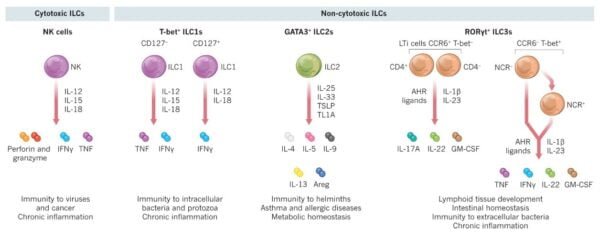
2. Key Capabilities of ILCs
- Cytokine Manufacturing: ILCs produce a variety of cytokines, together with interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), interleukin-5 (IL-5), and interleukin-13 (IL-13). These cytokines assist regulate immune responses and irritation. For example, IFN-γ performs a crucial position in enhancing the power of different immune cells to fight infections.
- Antiviral Mechanisms: By producing antiviral cytokines and upregulating genes concerned in antiviral protection, ILCs contribute to elevated resistance of mucosal surfaces to viral infections. This operate is essential in sustaining mucosal immunity and stopping pathogen entry.
Abstract
Innate immunity is the physique’s preliminary and broad-spectrum protection mechanism in opposition to infections and accidents. It entails a variety of elements, together with ILCs, NK cells, and numerous inner and exterior protection mechanisms. Whereas innate immunity lacks the specificity of adaptive immunity, it performs an important position in offering fast safety and setting the stage for the adaptive immune response.
By understanding the features and interactions of innate immune cells and mechanisms, we achieve perception into how the physique defends itself in opposition to illness and the way these processes could be utilized or modified in medical analysis and therapy methods.
References
- Janeway, C. A., Travers, P., Walport, M., & Shlomchik, M. J. (2001). Immunobiology: The Immune System in Well being and Illness. fifth Version. Garland Science.
- Medzhitov, R., & Janeway, C. A. (2000). “Innate Immunity.” New England Journal of Medication, 343(5), 338-344.
- Gordon, S. (2002). “Pattern Recognition Receptors: Doubling Up on Detection.” Nature Opinions Immunology, 2(5), 332-341.
- Klose, C. S. N., & Artis, D. (2020). “Innate Lymphoid Cells as Regulators of Immunity, Inflammation, and Tissue Homeostasis.” Nature Immunology, 21(5), 498-508.
- Murphy, Ok., & Weaver, C. (2016). Janeway’s Immunobiology. ninth Version. Garland Science.
- Takeda, Ok., & Akira, S. (2004). “Toll-Like Receptors in Innate Immunity.” Worldwide Immunology, 16(1), 1-14.
- Bianchi, M. E. (2007). “DAMPs, PAMPs, and Alarmins: All We Need to Know About Danger.” Journal of Leukocyte Biology, 81(1), 1-5.

