Pascal Michaillat (UCSC) and Emmanuel Saez (UC Berkeley) say 40% chance, sure. From the summary to the paper:
To reply this query, we develop a brand new Sahm-type recession indicator that mixes emptiness and unemployment information. The indicator is the minimal of the Sahm indicator— the distinction between the 3-month trailing common of the unemployment charge and its minimal over the previous 12 months—and an analogous indicator constructed with the emptiness charge—the distinction between the 3-month trailing common of the emptiness charge and its most over the previous 12 months. We then suggest a two-sided recession rule: When our indicator reaches 0.3pp, a recession could have began; when the indicator reaches 0.8pp, a recession has began for certain. This new rule is triggered sooner than the Sahm rule: on common it detects recessions 1.4 months after they’ve began, whereas the Sahm rule detects them 2.6 months after their begin. The brand new rule additionally has a greater historic monitor report: it completely identifies all recessions since 1930, whereas the Sahm rule breaks down earlier than 1960. With July 2024 information, our indicator is at 0.5pp, so the chance that the US financial system is now in recession is 40%. In actual fact, the recession could have began as early as March 2024.
Supply: Michaillat and Saez (2024).
So far as I can inform, the authors use ultimate revised information, not realtime. It will be good to see if the outcomes had been strong to using realtime information, given the huge impact of inhabitants controls particularly lately.
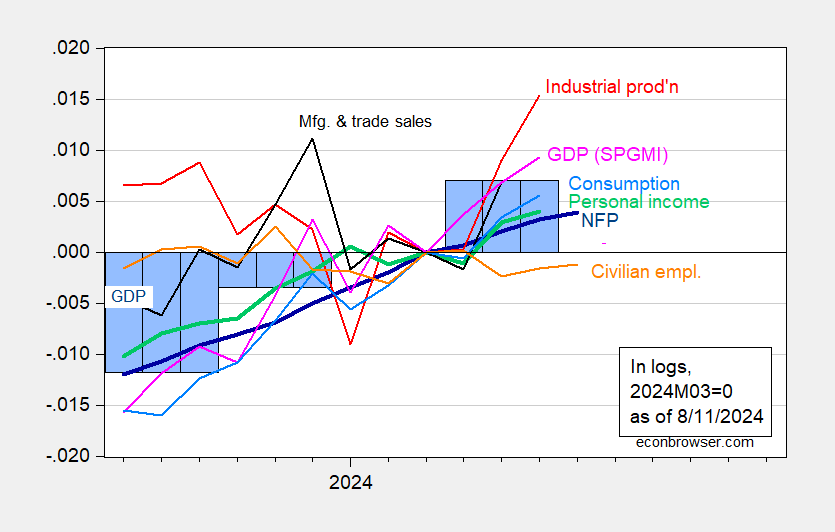
Normalizing NBER indicators to 2024M03 as a peak, we’ve got Determine 1:
Determine 1 [corrected 8/13]: Nonfarm Payroll (NFP) employment from CES (daring blue), civilian employment (orange), industrial manufacturing (pink), private revenue excluding present transfers in Ch.2017$ (daring inexperienced), manufacturing and commerce gross sales in Ch.2017$ (black), consumption in Ch.2017$ (mild blue), and month-to-month GDP in Ch.2017$ (pink), GDP (blue bars), all log normalized to 2023M04=0. Supply: BLS by way of FRED, Federal Reserve, BEA 2024Q2 advance launch, S&P International Market Insights (nee Macroeconomic Advisers, IHS Markit) (8/1/2024 launch), and writer’s calculations.
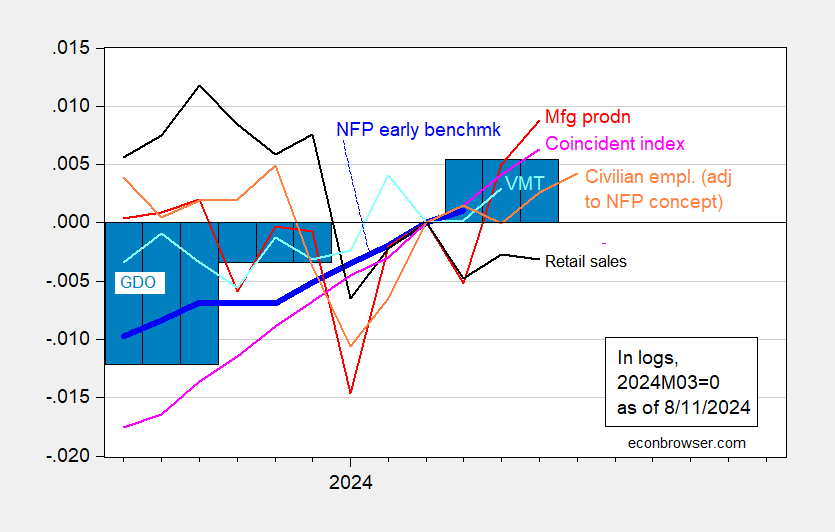
And different indicators:
Determine 2: Nonfarm Payroll (NFP) employment Philadelphia Fed early benchmark (daring blue), civilian employment adjusted to NFP idea (orange), manufacturing manufacturing (pink), retail gross sales (black), car miles traveled (mild blue), and Coincident Index (mild pink), GDO (blue bars), all log normalized to 2023M04=0. GDI utilized in calculating GDO for 2024Q2 estimated by predicting 2024Q2 web working surplus utilizing GDP, lagged surplus, lagged differenced surplus, 2021Q1-2024Q1.Supply: BLS by way of FRED, Federal Reserve, BEA 2024Q2 advance launch, Philadelphia Fed, and writer’s calculations.
After all, all these collection might be revised to various levels, with GDP being the collection at biggest threat — which is why NBER’s BCDC doesn’t put major weight on it.