Picture by pch.vector on Freepik
Hello everybody! I’m certain you’re studying this text as a result of you have an interest in a machine-learning mannequin and need to construct one.
You might have tried to develop machine studying fashions earlier than or you’re totally new to the idea. Irrespective of your expertise, this text will information you thru the very best practices for creating machine studying fashions.
On this article, we are going to develop a Buyer Churn prediction classification mannequin following the steps beneath:
1. Enterprise Understanding
2. Information Assortment and Preparation
- Accumulating Information
- Exploratory Information Evaluation (EDA) and Information Cleansing
- Function Choice
3. Constructing the Machine Studying Mannequin
- Selecting the Proper Mannequin
- Splitting the Information
- Coaching the Mannequin
- Mannequin Analysis
4. Mannequin Optimization
5. Deploying the Mannequin
Let’s get into it if you’re enthusiastic about constructing your first machine studying mannequin.
Understanding the Fundamentals
Earlier than we get into the machine studying mannequin growth, let’s briefly clarify machine studying, the varieties of machine studying, and some terminologies we are going to use on this article.
First, let’s talk about the varieties of machine studying fashions we are able to develop. 4 most important varieties of Machine Studying typically developed are:
- Supervised Machine Studying is a machine studying algorithm that learns from labeled datasets. Based mostly on the right output, the mannequin learns from the sample and tries to foretell the brand new knowledge. There are two classes in Supervised Machine Studying: Classification (Class prediction) and Regression (Numerical prediction).
- Unsupervised Machine Studying is an algorithm that tries to search out patterns in knowledge with out route. Not like supervised machine studying, the mannequin will not be guided by label knowledge. This kind has two widespread classes: Clustering (Information Segmentation) and Dimensionality Discount (Function Discount).
- Semi-supervised machine studying combines the labeled and unlabeled datasets, the place the labeled dataset guides the mannequin in figuring out patterns within the unlabeled knowledge. The best instance is a self-training mannequin that may label the unlabeled knowledge primarily based on a labeled knowledge sample.
- Reinforcement Studying is a machine studying algorithm that may work together with the atmosphere and react primarily based on the motion (getting a reward or punishment). It might maximize the consequence with the rewards system and keep away from dangerous outcomes with punishment. An instance of this mannequin utility is the self-driving automobile.
You additionally have to know a number of terminologies to develop a machine-learning mannequin:
- Options: Enter variables used to make predictions in a machine studying mannequin.
- Labels: Output variables that the mannequin is making an attempt to foretell.
- Information Splitting: The method of information separation into completely different units.
- Coaching Set: Information used to coach the machine studying mannequin.
- Check Set: Information used to guage the efficiency of the skilled mannequin.
- Validation Set: Information use used in the course of the coaching course of to tune hyperparameters
- Exploratory Information Evaluation (EDA): The method of analyzing and visualizing datasets to summarize their data and uncover patterns.
- Fashions: The result of the Machine Studying course of. They’re the mathematical illustration of the patterns and relationships throughout the knowledge.
- Overfitting: Happens when the mannequin is generalized too effectively and learns the information noise. The mannequin can predict effectively within the coaching however not within the take a look at set.
- Underfitting: When a mannequin is just too easy to seize the underlying patterns within the knowledge. The mannequin efficiency in coaching and take a look at units could possibly be higher.
- Hyperparameters: Configuration settings are used to tune the mannequin and are set earlier than coaching begins.
- Cross-validation: a method for evaluating the mannequin by partitioning the unique pattern into coaching and validation units a number of instances.
- Function Engineering: Utilizing area information to get new options from uncooked knowledge.
- Mannequin Coaching: The method of studying the parameters of a mannequin utilizing the coaching knowledge.
- Mannequin Analysis: Assessing the efficiency of a skilled mannequin utilizing machine studying metrics like accuracy, precision, and recall.
- Mannequin Deployment: Making a skilled mannequin out there in a manufacturing atmosphere.
With all this fundamental information, let’s study to develop our first machine-learning mannequin.
1. Enterprise Understanding
Earlier than any machine studying mannequin growth, we should perceive why we should develop the mannequin. That’s why understanding what the enterprise needs is critical to make sure the mannequin is legitimate.
Enterprise understanding normally requires a correct dialogue with the associated stakeholders. Nonetheless, since this tutorial doesn’t have enterprise customers for the machine studying mannequin, we assume the enterprise wants ourselves.
As acknowledged beforehand, we’d develop a Buyer Churn prediction mannequin. On this case, the enterprise must keep away from additional churn from the corporate and desires to take motion for the client with a excessive likelihood of churning.
With the above enterprise necessities, we want particular metrics to measure whether or not the mannequin performs effectively. There are lots of measurements, however I suggest utilizing the Recall metric.
In financial values, it is perhaps extra useful to make use of Recall, because it tries to attenuate the False Unfavourable or lower the quantity of prediction that was not churning whereas it’s churning. After all, we are able to attempt to purpose for steadiness by utilizing the F1 metric.
With that in thoughts, let’s get into the primary a part of our tutorial.
2. Information Assortment and Preparation
Information Assortment
Information is the guts of any machine studying mission. With out it, we are able to’t have a machine studying mannequin to coach. That’s why we want high quality knowledge with correct preparation earlier than we enter them into the machine studying algorithm.
In a real-world case, clear knowledge doesn’t come simply. Usually, we have to acquire it by means of purposes, surveys, and plenty of different sources earlier than storing it in knowledge storage. Nonetheless, this tutorial solely covers accumulating the dataset as we use the present clear knowledge.
In our case, we’d use the Telco Buyer Churn knowledge from the Kaggle. It’s open-source classification knowledge concerning buyer historical past within the telco business with the churn label.
Exploratory Information Evaluation (EDA) and Information Cleansing
Let’s begin by reviewing our dataset. I assume the reader already has fundamental Python information and may use Python packages of their pocket book. I additionally primarily based the tutorial on Anaconda atmosphere distribution to make issues simpler.
To grasp the information we’ve, we have to load it right into a Python bundle for knowledge manipulation. Probably the most well-known one is the Pandas Python bundle, which we are going to use. We will use the next code to load and overview the CSV knowledge.
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('WA_Fn-UseC_-Telco-Buyer-Churn.csv')
df.head()
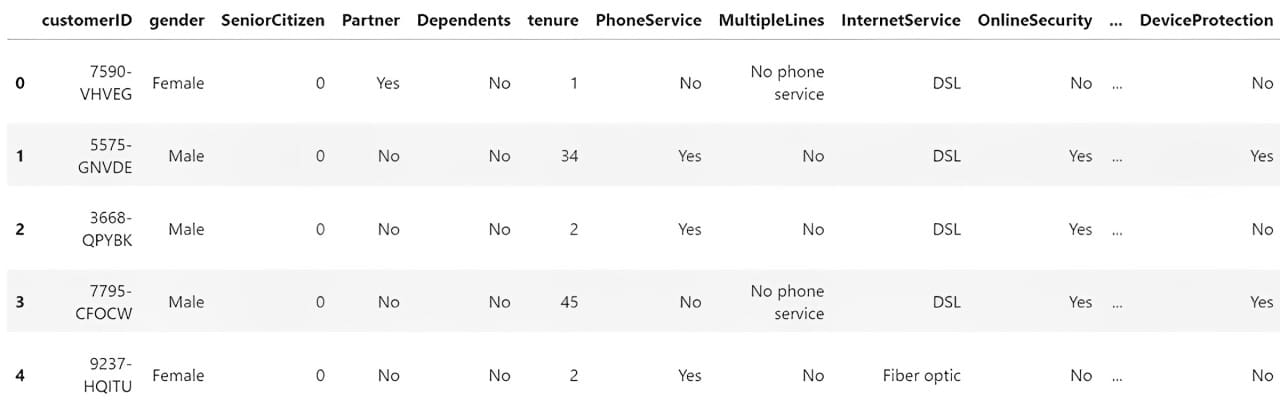
Subsequent, we’d discover the information to grasp our dataset. Listed here are a number of actions that we’d carry out for the EDA course of.
1. Analyzing the options and the abstract statistics.
2. Checks for lacking values within the options.
3. Analyze the distribution of the label (Churn).
4. Plots histograms for numerical options and bar plots for categorical options.
5. Plots a correlation heatmap for numerical options.
6. Makes use of field plots to establish distributions and potential outliers.
First, we’d test the options and abstract statistics. With Pandas, we are able to see our dataset options utilizing the next code.
# Get the essential details about the dataset
df.information()
Output>>
RangeIndex: 7043 entries, 0 to 7042
Information columns (whole 21 columns):
# Column Non-Null Rely Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 customerID 7043 non-null object
1 gender 7043 non-null object
2 SeniorCitizen 7043 non-null int64
3 Accomplice 7043 non-null object
4 Dependents 7043 non-null object
5 tenure 7043 non-null int64
6 PhoneService 7043 non-null object
7 MultipleLines 7043 non-null object
8 InternetService 7043 non-null object
9 OnlineSecurity 7043 non-null object
10 OnlineBackup 7043 non-null object
11 DeviceProtection 7043 non-null object
12 TechSupport 7043 non-null object
13 StreamingTV 7043 non-null object
14 StreamingMovies 7043 non-null object
15 Contract 7043 non-null object
16 PaperlessBilling 7043 non-null object
17 PaymentMethod 7043 non-null object
18 MonthlyCharges 7043 non-null float64
19 TotalCharges 7043 non-null object
20 Churn 7043 non-null object
dtypes: float64(1), int64(2), object(18)
reminiscence utilization: 1.1+ MB
We’d additionally get the dataset abstract statistics with the next code.
# Get the numerical abstract statistics of the dataset
df.describe()
# Get the explicit abstract statistics of the dataset
df.describe(exclude="number")
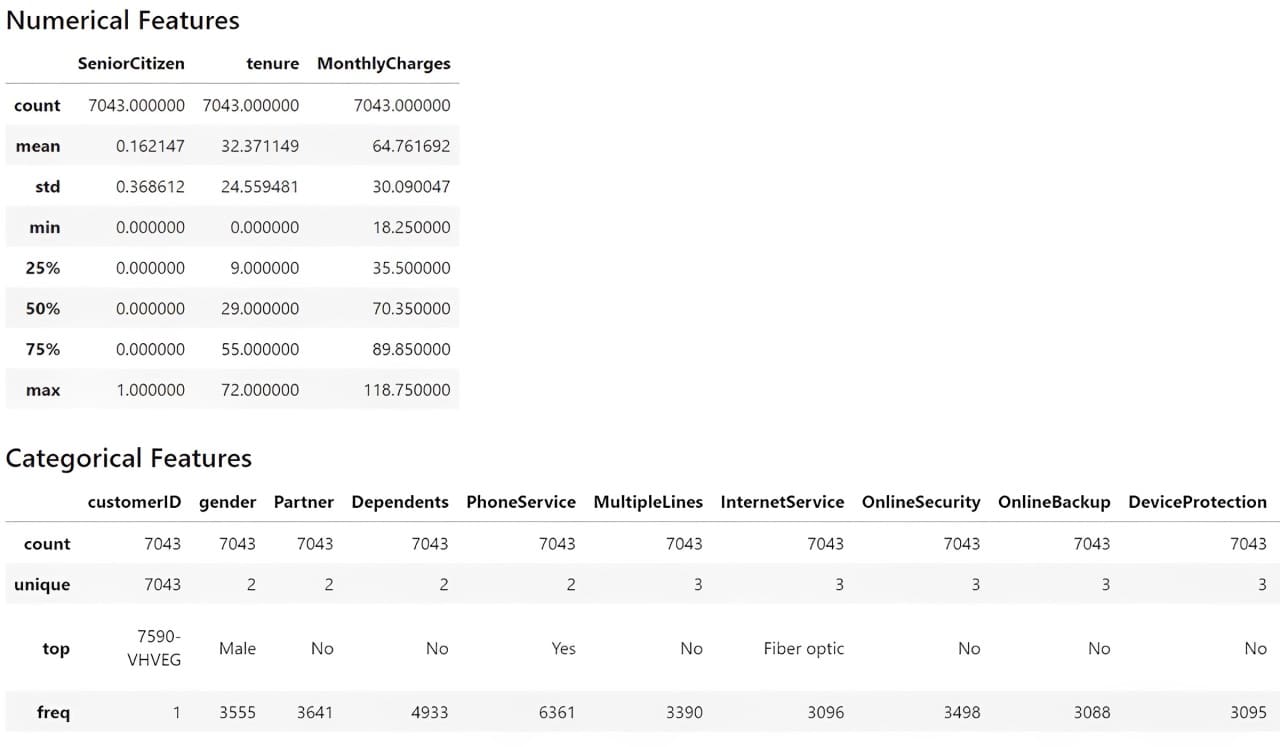
From the data above, we perceive that we’ve 19 options with one goal function (Churn). The dataset accommodates 7043 rows, and most datasets are categorical.
Let’s test for the lacking knowledge.
# Test for lacking values
print(df.isnull().sum())
Output>>
Lacking Values:
customerID 0
gender 0
SeniorCitizen 0
Accomplice 0
Dependents 0
tenure 0
PhoneService 0
MultipleLines 0
InternetService 0
OnlineSecurity 0
OnlineBackup 0
DeviceProtection 0
TechSupport 0
StreamingTV 0
StreamingMovies 0
Contract 0
PaperlessBilling 0
PaymentMethod 0
MonthlyCharges 0
TotalCharges 0
Churn 0
Our dataset doesn’t comprise lacking knowledge, so we don’t have to carry out any lacking knowledge therapy exercise.
Then, we’d test the goal variable to see if we’ve an imbalance case.
print(df['Churn'].value_counts())
Output>>
Distribution of Goal Variable:
No 5174
Sure 1869
There’s a slight imbalance, as solely near 25% of the churn happens in comparison with the non-churn circumstances.
Let’s additionally see the distribution of the opposite options, beginning with the numerical options. Nonetheless, we’d additionally rework the TotalCharges function right into a numerical column, as this function needs to be numerical slightly than a class. Moreover, the SeniorCitizen function needs to be categorical in order that I might rework it into strings. Additionally, because the Churn function is categorical, we’d develop new options that present it as a numerical column.
import numpy as np
df['TotalCharges'] = df['TotalCharges'].change('', np.nan)
df['TotalCharges'] = pd.to_numeric(df['TotalCharges'], errors="coerce").fillna(0)
df['SeniorCitizen'] = df['SeniorCitizen'].astype('str')
df['ChurnTarget'] = df['Churn'].apply(lambda x: 1 if x=='Sure' else 0)
df['ChurnTarget'] = df['Churn'].apply(lambda x: 1 if x=='Sure' else 0)
num_features = df.select_dtypes('quantity').columns
df[num_features].hist(bins=15, figsize=(15, 6), format=(2, 5))

We’d additionally present categorical function plotting apart from the customerID, as they’re identifiers with distinctive values.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Plot distribution of categorical options
cat_features = df.drop('customerID', axis =1).select_dtypes(embrace="object").columns
plt.determine(figsize=(20, 20))
for i, col in enumerate(cat_features, 1):
plt.subplot(5, 4, i)
df[col].value_counts().plot(type='bar')
plt.title(col)

We then would see the correlation between numerical options with the next code.
import seaborn as sns
# Plot correlations between numerical options
plt.determine(figsize=(10, 8))
sns.heatmap(df[num_features].corr())
plt.title('Correlation Heatmap')

The correlation above is predicated on the Pearson Correlation, a linear correlation between one function and the opposite. We will additionally carry out correlation evaluation to categorical evaluation with Cramer’s V. To make the evaluation simpler, we’d set up Dython Python bundle that would assist our evaluation.
As soon as the bundle is put in, we are going to carry out the correlation evaluation with the next code.
from dython.nominal import associations
# Calculate the Cramer’s V and correlation matrix
assoc = associations(df[cat_features], nominal_columns="all", plot=False)
corr_matrix = assoc['corr']
# Plot the heatmap
plt.determine(figsize=(14, 12))
sns.heatmap(corr_matrix)

Lastly, we’d test the numerical outlier with a field plot primarily based on the Interquartile Vary (IQR).
# Plot field plots to establish outliers
plt.determine(figsize=(20, 15))
for i, col in enumerate(num_features, 1):
plt.subplot(4, 4, i)
sns.boxplot(y=df[col])
plt.title(col)

From the evaluation above, we are able to see that we must always handle no lacking knowledge or outliers. The following step is to carry out function choice for our machine studying mannequin, as we solely need the options that influence the prediction and are viable within the enterprise.
Function Choice
There are lots of methods to carry out function choice, normally executed by combining enterprise information and technical utility. Nonetheless, this tutorial will solely use the correlation evaluation we’ve executed beforehand to make the function choice.
First, let’s choose the numerical options primarily based on the correlation evaluation.
goal="ChurnTarget"
num_features = df.select_dtypes(embrace=[np.number]).columns.drop(goal)
# Calculate correlations
correlations = df[num_features].corrwith(df[target])
# Set a threshold for function choice
threshold = 0.3
selected_num_features = correlations[abs(correlations) > threshold].index.tolist()
You’ll be able to mess around with the edge later to see if the function choice impacts the mannequin’s efficiency. We’d additionally carry out the function choice into the explicit options.
categorical_target="Churn"
assoc = associations(df[cat_features], nominal_columns="all", plot=False)
corr_matrix = assoc['corr']
threshold = 0.3
selected_cat_features = corr_matrix[corr_matrix.loc[categorical_target] > threshold ].index.tolist()
del selected_cat_features[-1]
Then, we’d mix all the chosen options with the next code.
selected_features = []
selected_features.prolong(selected_num_features)
selected_features.prolong(selected_cat_features)
print(selected_features)
Output>>
['tenure',
'InternetService',
'OnlineSecurity',
'TechSupport',
'Contract',
'PaymentMethod']
In the long run, we’ve six options that might be used to develop the client churn machine studying mannequin.
3. Constructing the Machine Studying Mannequin
Selecting the Proper Mannequin
There are lots of issues to picking an appropriate mannequin for machine studying growth, but it surely at all times relies on the enterprise wants. A couple of factors to recollect:
- The use case downside. Is it supervised or unsupervised, or is it classification or regression? Is it Multiclass or Multilabel? The case downside would dictate which mannequin can be utilized.
- The information traits. Is it tabular knowledge, textual content, or picture? Is the dataset measurement massive or small? Did the dataset comprise lacking values? Relying on the dataset, the mannequin we select could possibly be completely different.
- How simple is the mannequin to be interpreted? Balancing interpretability and efficiency is important for the enterprise.
As a thumb rule, beginning with an easier mannequin as a benchmark is usually finest earlier than continuing to a fancy one. You’ll be able to learn my earlier article concerning the easy mannequin to grasp what constitutes a easy mannequin.
For this tutorial, let’s begin with linear mannequin Logistic Regression for the mannequin growth.
Splitting the Information
The following exercise is to separate the information into coaching, take a look at, and validation units. The aim of information splitting throughout machine studying mannequin coaching is to have a knowledge set that acts as unseen knowledge (real-world knowledge) to guage the mannequin unbias with none knowledge leakage.
To separate the information, we are going to use the next code:
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
goal="ChurnTarget"
X = df[selected_features]
y = df[target]
cat_features = X.select_dtypes(embrace=['object']).columns.tolist()
num_features = X.select_dtypes(embrace=['number']).columns.tolist()
#Splitting knowledge into Prepare, Validation, and Check Set
X_train_val, X_test, y_train_val, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42, stratify=y)
X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(X_train_val, y_train_val, test_size=0.25, random_state=42, stratify=y_train_val)
Within the above code, we cut up the information into 60% of the coaching dataset and 20% of the take a look at and validation set. As soon as we’ve the dataset, we are going to prepare the mannequin.
Coaching the Mannequin
As talked about, we’d prepare a Logistic Regression mannequin with our coaching knowledge. Nonetheless, the mannequin can solely settle for numerical knowledge, so we should preprocess the dataset. This implies we have to rework the explicit knowledge into numerical knowledge.
For finest apply, we additionally use the Scikit-Be taught pipeline to comprise all of the preprocessing and modeling steps. The next code lets you do this.
from sklearn.compose import ColumnTransformer
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
# Put together the preprocessing step
preprocessor = ColumnTransformer(
transformers=[
('num', 'passthrough', num_features),
('cat', OneHotEncoder(), cat_features)
])
pipeline = Pipeline(steps=[
('preprocessor', preprocessor),
('classifier', LogisticRegression(max_iter=1000))
])
# Prepare the logistic regression mannequin
pipeline.match(X_train, y_train)
The mannequin pipeline would appear to be the picture beneath.

The Scikit-Be taught pipeline would settle for the unseen knowledge and undergo all of the preprocessing steps earlier than coming into the mannequin. After the mannequin is completed coaching, let’s consider our mannequin consequence.
Mannequin Analysis
As talked about, we are going to consider the mannequin by specializing in the Recall metrics. Nonetheless, the next code exhibits all the essential classification metrics.
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
# Consider on the validation set
y_val_pred = pipeline.predict(X_val)
print("Validation Classification Report:n", classification_report(y_val, y_val_pred))
# Consider on the take a look at set
y_test_pred = pipeline.predict(X_test)
print("Test Classification Report:n", classification_report(y_test, y_test_pred))

As we are able to see from the Validation and Check knowledge, the Recall for churn (1) will not be the very best. That’s why we are able to optimize the mannequin to get the very best consequence.
4. Mannequin Optimization
We at all times have to give attention to the information to get the very best consequence. Nonetheless, optimizing the mannequin may additionally result in higher outcomes. This is the reason we are able to optimize our mannequin. One method to optimize the mannequin is through hyperparameter optimization, which exams all mixtures of those mannequin hyperparameters to search out the very best one primarily based on the metrics.
Each mannequin has a set of hyperparameters we are able to set earlier than coaching it. We name hyperparameter optimization the experiment to see which mixture is the very best. To try this, we are able to use the next code.
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
# Outline the logistic regression mannequin inside a pipeline
pipeline = Pipeline(steps=[
('preprocessor', preprocessor),
('classifier', LogisticRegression(max_iter=1000))
])
# Outline the hyperparameters for GridSearchCV
param_grid = {
'classifier__C': [0.1, 1, 10, 100],
'classifier__solver': ['lbfgs', 'liblinear']
}
# Carry out Grid Search with cross-validation
grid_search = GridSearchCV(pipeline, param_grid, cv=5, scoring='recall')
grid_search.match(X_train, y_train)
# Greatest hyperparameters
print("Best Hyperparameters:", grid_search.best_params_)
# Consider on the validation set
y_val_pred = grid_search.predict(X_val)
print("Validation Classification Report:n", classification_report(y_val, y_val_pred))
# Consider on the take a look at set
y_test_pred = grid_search.predict(X_test)
print("Test Classification Report:n", classification_report(y_test, y_test_pred))

The outcomes nonetheless don’t present the very best recall rating, however that is anticipated as they’re solely the baseline mannequin. Let’s experiment with a number of fashions to see if the Recall efficiency improves. You’ll be able to at all times tweak the hyperparameter beneath.
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier, GradientBoostingClassifier
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from xgboost import XGBClassifier
from lightgbm import LGBMClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import recall_score
# Outline the fashions and their parameter grids
fashions = {
'Logistic Regression': {
'mannequin': LogisticRegression(max_iter=1000),
'params': {
'classifier__C': [0.1, 1, 10, 100],
'classifier__solver': ['lbfgs', 'liblinear']
}
},
'Choice Tree': {
'mannequin': DecisionTreeClassifier(),
'params': {
'classifier__max_depth': [None, 10, 20, 30],
'classifier__min_samples_split': [2, 10, 20]
}
},
'Random Forest': {
'mannequin': RandomForestClassifier(),
'params': {
'classifier__n_estimators': [100, 200],
'classifier__max_depth': [None, 10, 20]
}
},
'SVM': {
'mannequin': SVC(),
'params': {
'classifier__C': [0.1, 1, 10, 100],
'classifier__kernel': ['linear', 'rbf']
}
},
'Gradient Boosting': {
'mannequin': GradientBoostingClassifier(),
'params': {
'classifier__n_estimators': [100, 200],
'classifier__learning_rate': [0.01, 0.1, 0.2]
}
},
'XGBoost': {
'mannequin': XGBClassifier(use_label_encoder=False, eval_metric="logloss"),
'params': {
'classifier__n_estimators': [100, 200],
'classifier__learning_rate': [0.01, 0.1, 0.2],
'classifier__max_depth': [3, 6, 9]
}
},
'LightGBM': {
'mannequin': LGBMClassifier(),
'params': {
'classifier__n_estimators': [100, 200],
'classifier__learning_rate': [0.01, 0.1, 0.2],
'classifier__num_leaves': [31, 50, 100]
}
}
}
outcomes = []
# Prepare and consider every mannequin
for model_name, model_info in fashions.gadgets():
pipeline = Pipeline(steps=[
('preprocessor', preprocessor),
('classifier', model_info['model'])
])
grid_search = GridSearchCV(pipeline, model_info['params'], cv=5, scoring='recall')
grid_search.match(X_train, y_train)
# Greatest mannequin from Grid Search
best_model = grid_search.best_estimator_
# Consider on the validation set
y_val_pred = best_model.predict(X_val)
val_recall = recall_score(y_val, y_val_pred, pos_label=1)
# Consider on the take a look at set
y_test_pred = best_model.predict(X_test)
test_recall = recall_score(y_test, y_test_pred, pos_label=1)
# Save outcomes
outcomes.append({
'mannequin': model_name,
'best_params': grid_search.best_params_,
'val_recall': val_recall,
'test_recall': test_recall,
'classification_report_val': classification_report(y_val, y_val_pred),
'classification_report_test': classification_report(y_test, y_test_pred)
})
# Plot the take a look at recall scores
plt.determine(figsize=(10, 6))
model_names = [result['model'] for lead to outcomes]
test_recalls = [result['test_recall'] for lead to outcomes]
plt.barh(model_names, test_recalls, colour="skyblue")
plt.xlabel('Check Recall')
plt.title('Comparability of Check Recall for Totally different Fashions')
plt.present()

The recall consequence has not modified a lot; even the baseline Logistic Regression appears the very best. We should always return with a greater function choice if we would like a greater consequence.
Nonetheless, let’s transfer ahead with the present Logistic Regression mannequin and attempt to deploy them.
5. Deploying the Mannequin
We’ve constructed our machine studying mannequin. After having the mannequin, the following step is to deploy it into manufacturing. Let’s simulate it utilizing a easy API.
First, let’s develop our mannequin once more and put it aside as a joblib object.
import joblib
best_params = {'classifier__C': 1, 'classifier__solver': 'lbfgs'}
logreg_model = LogisticRegression(C=best_params['classifier__C'], solver=best_params['classifier__solver'], max_iter=1000)
preprocessor = ColumnTransformer(
transformers=[
('num', 'passthrough', num_features),
('cat', OneHotEncoder(), cat_features)
pipeline = Pipeline(steps=[
('preprocessor', preprocessor),
('classifier', logreg_model)
])
pipeline.match(X_train, y_train)
# Save the mannequin
joblib.dump(pipeline, 'logreg_model.joblib')
As soon as the mannequin object is prepared, we are going to transfer right into a Python script to create the API. However first, we have to set up a number of packages used for deployment.
pip set up fastapi uvicorn
We’d not do it within the pocket book however in an IDE reminiscent of Visible Studio Code. In your most well-liked IDE, create a Python script known as app.py and put the code beneath into the script.
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
import joblib
import numpy as np
# Load the logistic regression mannequin pipeline
mannequin = joblib.load('logreg_model.joblib')
# Outline the enter knowledge for mannequin
class CustomerData(BaseModel):
tenure: int
InternetService: str
OnlineSecurity: str
TechSupport: str
Contract: str
PaymentMethod: str
# Create FastAPI app
app = FastAPI()
# Outline prediction endpoint
@app.submit("/predict")
def predict(knowledge: CustomerData):
# Convert enter knowledge to a dictionary after which to a DataFrame
input_data = {
'tenure': [data.tenure],
'InternetService': [data.InternetService],
'OnlineSecurity': [data.OnlineSecurity],
'TechSupport': [data.TechSupport],
'Contract': [data.Contract],
'PaymentMethod': [data.PaymentMethod]
}
import pandas as pd
input_df = pd.DataFrame(input_data)
# Make a prediction
prediction = mannequin.predict(input_df)
# Return the prediction
return {"prediction": int(prediction[0])}
if __name__ == "__main__":
import uvicorn
uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=8000)
In your command immediate or terminal, run the next code.
With the code above, we have already got an API to simply accept knowledge and create predictions. Let’s strive it out with the next code within the new terminal.
curl -X POST "http://127.0.0.1:8000/predict" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d "{"tenure": 72, "InternetService": "Fiber optic", "OnlineSecurity": "Sure", "TechSupport": "Sure", "Contract": "Two 12 months", "PaymentMethod": "Bank card (computerized)"}"
Output>>
{"prediction":0}
As you possibly can see, the API result’s a dictionary with prediction 0 (Not-Churn). You’ll be able to tweak the code even additional to get the specified consequence.
Congratulation. You’ve gotten developed your machine studying mannequin and efficiently deployed it within the API.
Conclusion
We’ve discovered how one can develop a machine studying mannequin from the start to the deployment. Experiment with different datasets and use circumstances to get the sensation even higher. All of the code this text makes use of will likely be out there on my GitHub repository.
Cornellius Yudha Wijaya is a knowledge science assistant supervisor and knowledge author. Whereas working full-time at Allianz Indonesia, he likes to share Python and knowledge ideas through social media and writing media. Cornellius writes on quite a lot of AI and machine studying subjects.

